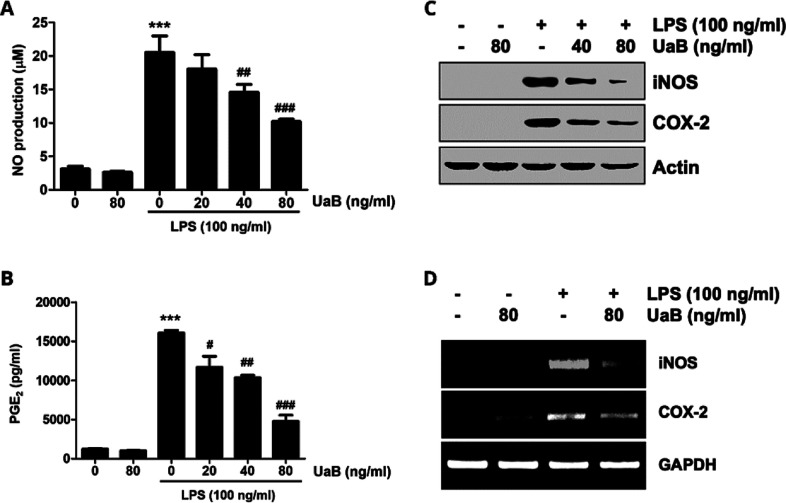
Figure 2.
Inhibition of NO and PGE2 production by UaB fraction in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. RAW 264.7 cells were incubated for 1 h with the indicated concentrations of UaB prior to stimulation with 100 ng/mL LPS for 24 h (A and B). The amounts of NO (A) and PGE2 (B) in the culture supernatants were determined via the Griess reaction and a commercial ELISA kit, respectively. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD of results from three independent experiments. ***p < 0.0001 vs controls (UaB- and LPS-untreated cells); ##p < 0.001 and ###p < 0.0001 vs cells cultured with 100 ng/mL LPS. Total protein was isolated from RAW 264.7 cells pretreated with the indicated concentrations of UaB followed by treatment with 100 ng/mL LPS for 24 h and subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Western blot analysis was performed using the indicated antibodies and an enhanced chemiluminescence detection system (C). RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with various concentrations of UaB for 1 h followed by treatment with 100 ng/mL LPS for 24 h. The total RNA was isolated, and the mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and COX-2 was analyzed using RT-PCR (D). The experiments were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained. Actin and GAPDH were used as internal controls for the western blot and the RT-PCR assays, respectively. NO, nitric oxide; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; iNOS, inducible NO synthase; and COX, cyclooxygenase.