Figure 4.
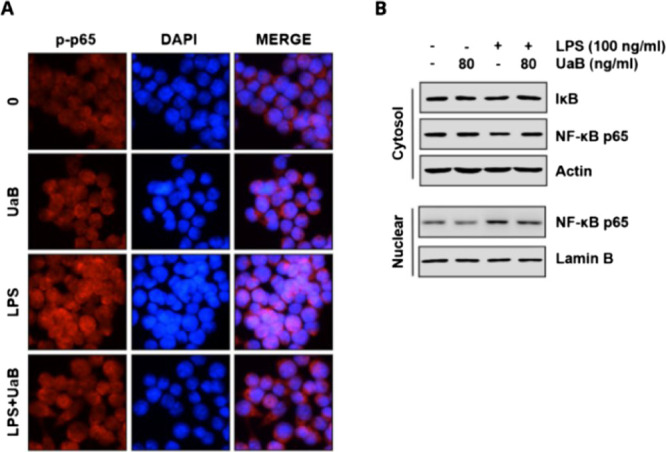
Effect of UaB fraction on LPS-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 macrophages. The cells were treated with 80 ng/mL UaB for 1 h prior to treatment with 100 ng/mL LPS for 30 min. Cells were pretreated with 80 ng/mL UaB for 1 h prior to stimulation with 100 ng/mL LPS for 30 min (A). Localization of NF-κB p65 was visualized following immunofluorescence staining with anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (red). The cells were also stained with DAPI for visualization of nuclei (blue). The cells were visualized using a fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×400). Cells were pretreated with 80 ng/mL UaB for 1 h prior to stimulation with 100 ng/mL LPS for 30 min (B). Nuclear and cytosolic proteins were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis using anti-NF-κB p65 and IκB antibodies. Lamin B and actin were used as internal controls for the nuclear and cytosolic fractions, respectively. NF, nuclear factor; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; and LPS, lipopolysaccharide.
