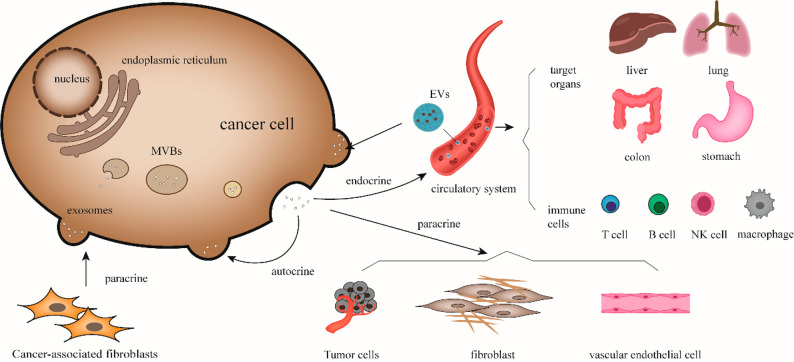
Figure 1.
Biological regulation of exosomes on cancer cell. Exosomes released from cancer cells can act on neighboring tumor cells, vascular endothelial cells, and fibroblasts through paracrine secretion. They can also act on themselves through autocrine release of exosomes carrying signal molecules or enter the systemic circulation to target organs, such as liver, lung, colon, and stomach. They affect various immune cells and regulate the tumor microenvironment and the immune response of the body. Correspondingly, exosomes from external sources can act on cancer cells and promote their progression.