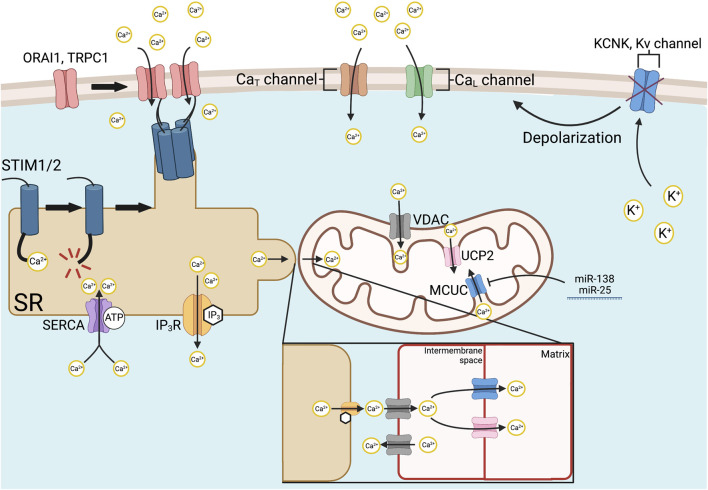
FIGURE 3.
Mechanisms of intracellular Ca2+ regulation. Store-operated Ca2+ entry is initiated via SR-bound STIM1 and STIM2, which have Ca2+-sensitive EF hand domains. Ca2+ store depletion from the SR causes STIM1/2 to aggregate at SR-plasma membrane junctions and recruits ORAI1, TRPC1, and other Ca2+ channels by its STIM1 ORAI activating region or CRAC activating domain. Various Ca2+ channels allow organellar uptake, such as SERCA and release, such as IP3Rs, respectively. Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake is mediated by the MCUC. The channel-forming subunit of the MCUC, MCU, is epigenetically downregulated in PAH by increased expression of miR-138 and miR-25. MCUC inhibition contributes to the Warburg effect by inactivating Ca2+-dependent enzymes that regulate OXPHOS within the mitochondria. In addition, reduced MCUC function increases cytosolic calcium, favoring vasoconstriction. Intramitochondrial calcium is also regulated, under certain conditions by the VDAC on the outer mitochondrial membrane, and UCP2, on the inner mitochondrial membrane. In PAH, voltage-gated Ca2+ entry is initiated by the inhibition and downregulated expression of redox-sensitive K+ channels, such as Kv1.5. The loss of tonic K+ efflux depolarizes the PASMC membrane potential, thereby activating L- and T-type Ca2+ channels and allowing influx of extracellular calcium down its 20,000/1 extracellular to intracellular concentration gradient. Abbreviations: CaL/T—L/T-type calcium channel; IP3R—Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; KCNK4—Potassium channel subfamily K member four; Kv—Voltage-gated potassium channel; MCUC—Mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex; OXPHOS—Oxidative phosphorylation; PAH—Pulmonary arterial hypertension; PASMC—Pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell; SERCA—Sarco (endo)plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; SR—Sarcoplasmic reticulum; ORAI1—Calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1; STIM1/2—Stromal interaction molecule 1/2; TRPC1—Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 1; UCP2—Uncoupling protein 2; VDAC—Voltage-dependent anion channel.