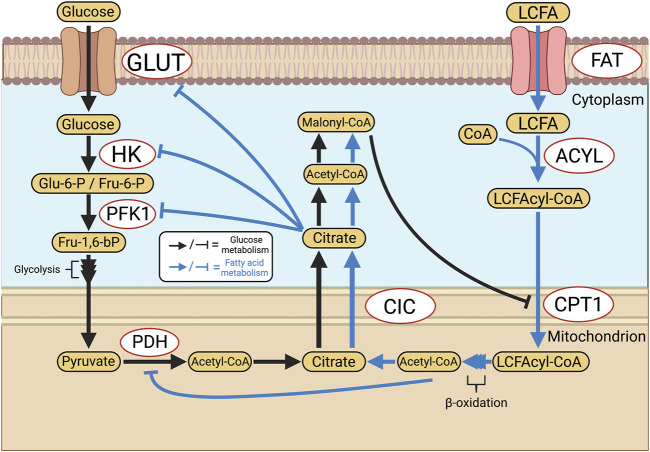
FIGURE 5.
Reciprocal inhibition of glucose and fatty acid oxidation: the Randle Cycle. The Randle cycle refers to the phenomenon that products of GO inhibit FAO and vice versa. FAO is inhibited by GO at the level of CPT1 and the import of long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria, thereby increasing levels of free fatty acids. In the cytosol GO is inhibited by citrate, which reduces cytoplasmic glycolysis, whilst in the mitochondria PDH is inhibited by FAO-derived, mitochondrial, acetyl-CoA. Abbreviations: ACYL—Long chain fatty acyl-CoA ligase; CIC—Citrate carrier; CPT1—Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; FAT—Fatty acid translocase; GLUT—Glucose transporter; HK—Hexokinase; LCFA—Long-chain fatty acid; PDH—Pyruvate dehydrogenase; PFK1—Phosphofructokinase 1; TTP—Tricarboxylate transport protein.