Fig. 3.
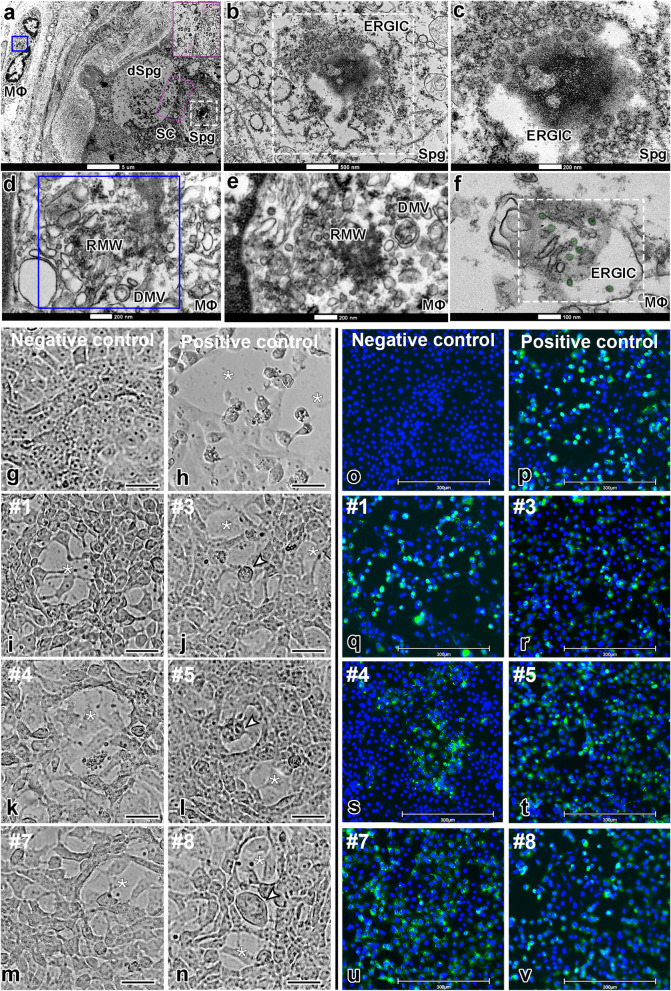
Infective SARS-CoV-2 particle formation and replication activity in Vero cells. a–f TEM images of testicular parenchyma (scale bars = a 5 μm; b 500 nm; c 200 nm; d 200 nm; e 200 nm; f 100 nm). a Altered seminiferous tubule cross-section, depicting a macrophage in tunica propria containing a replication membranous web (RMW; blue box) and a spermatogonial cell displaying an endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate complex (ERGIC, white box). The pink box indicates a spermatogonial cell clone surrounded by the cytoplasm of a Sertoli cell (labeled in pink). b, c Higher magnifications of spermatogonial cells showing structures similar to new virions inside the ERGIC. Although very large, this structure also resembles a hijacked nuclear pore complex (present in situations of viral replication). d Higher magnification of the RMW from the macrophage depicted in “figure a,” evidencing the presence of double-membrane vesicles (DMV). e–f Images from an interstitial macrophage presenting RMW, DMV, and ERGIC filled with new virions (labeled in green). g–n The cytopathic effect of SARS-CoV-2 was evaluated in VERO CCL-81 cells (empty area, *). Scale bars = 30 μm. g Cell confluence of VERO CCL-81 cultures before exposition to testicular macerates. h VERO CCL-81 cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 (positive control). i–n VERO CCL-81 cells exposed to testicular macerates of COVID-19 patients (empty area, *) (arrowheads indicate structures similar to a syncytium cell). Three wells were replicated per patient. o–v S-protein immunofluorescence in VERO CCL-81 cells (blue labeling: DAPI; green labeling: spike protein). Scale bars = 300 μm. o Negative control omitting the primary antibody. p Positive control using VERO CCL-81 cells infected with SARS-CoV-2. q–v Immunofluorescence in VERO CCL-81 cell culture after exposition to testicular homogenates