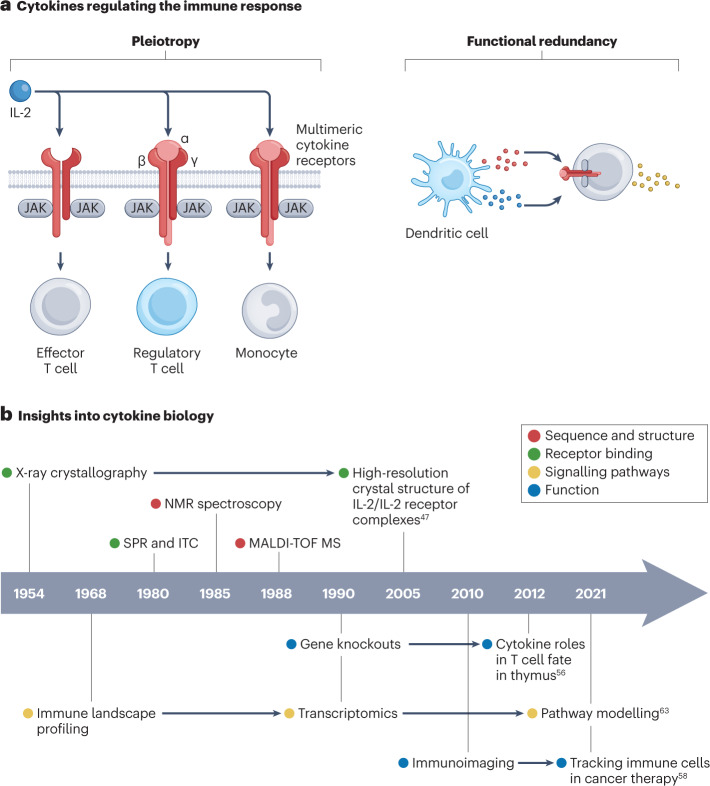
Fig. 1. Cytokine biology and mechanisms.
a, Cytokines are key regulators of the immune system and can be classified according to their function, for example, as pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory. Upon binding to the (multimeric) cytokine receptor on a target cell, cytokines can activate enzymes that regulate epigenetic modifications, cytokine synthesis, augmented metabolism, cellular proliferation and apoptosis. Cytokine pleiotropy refers to the ability to induce different phenotypic traits, resulting in a variety of biological consequences. The ability of cytokines to act on the same receptor indicates their redundancy. b, Insights into cytokine biology owing to advances in bioengineering, including greater knowledge about cytokine sequence and structure, receptor binding mechanisms, signalling pathways and function. Data are taken from refs. 47,56,58,63. ITC, isothermal titration calorimetry; JAK, Janus kinase; MALDI-TOF MS, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.