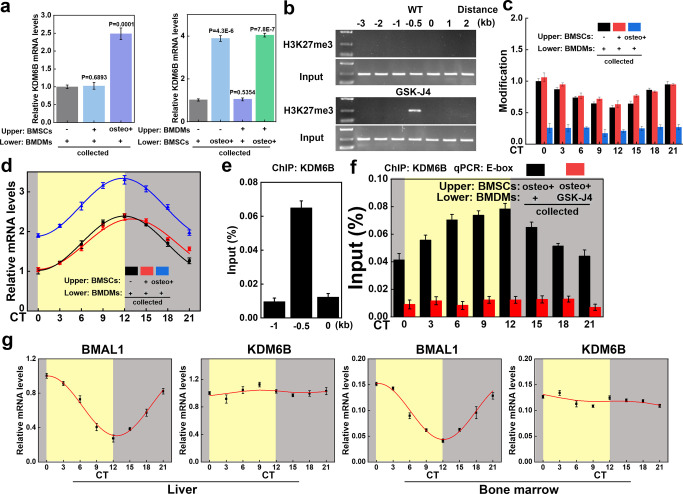
Figure 2.
KDM6B accumulated at the promoter region of BMAL1 in BMDMs during BMSC osteogenic differentiation. (a) BMSCs and BMDMs were extracted and seeded in the upper or lower chamber of Transwell plates. BMSC osteogenic differentiation culture medium was added (osteo+), and KDM6B mRNA expression levels were detected in all lower chambers via RT-qPCR. (b) The ChIP assay and DNA agarose gel electrophoresis were performed to test the binding level of H3K27me3 in the promoter region of BMAL1. (c) The ChIP assay was performed with synchronized mature BMDMs at specific intervals to show the circadian rhythm oscillation of H3K27me3 binding to the promoter region of BMAL1. (d) BMAL1 mRNA expression levels were also detected in all lower chambers via RT-qPCR. (e, f) The level of KDM6B binding to the promoter region of BMAL1 in BMDMs was increased when BMSCs in the upper chamber were osteogenically differentiated, whereas the addition of GSK-J4 led to the suppression of binding. (g) RT-qPCR was performed to investigate the circadian rhythm oscillation level of BMAL1 and KDM6B in the murine liver and bone marrow (circadian time (CT) 0–12: yellow background; CT12–24: gray background).