Fig. 7.
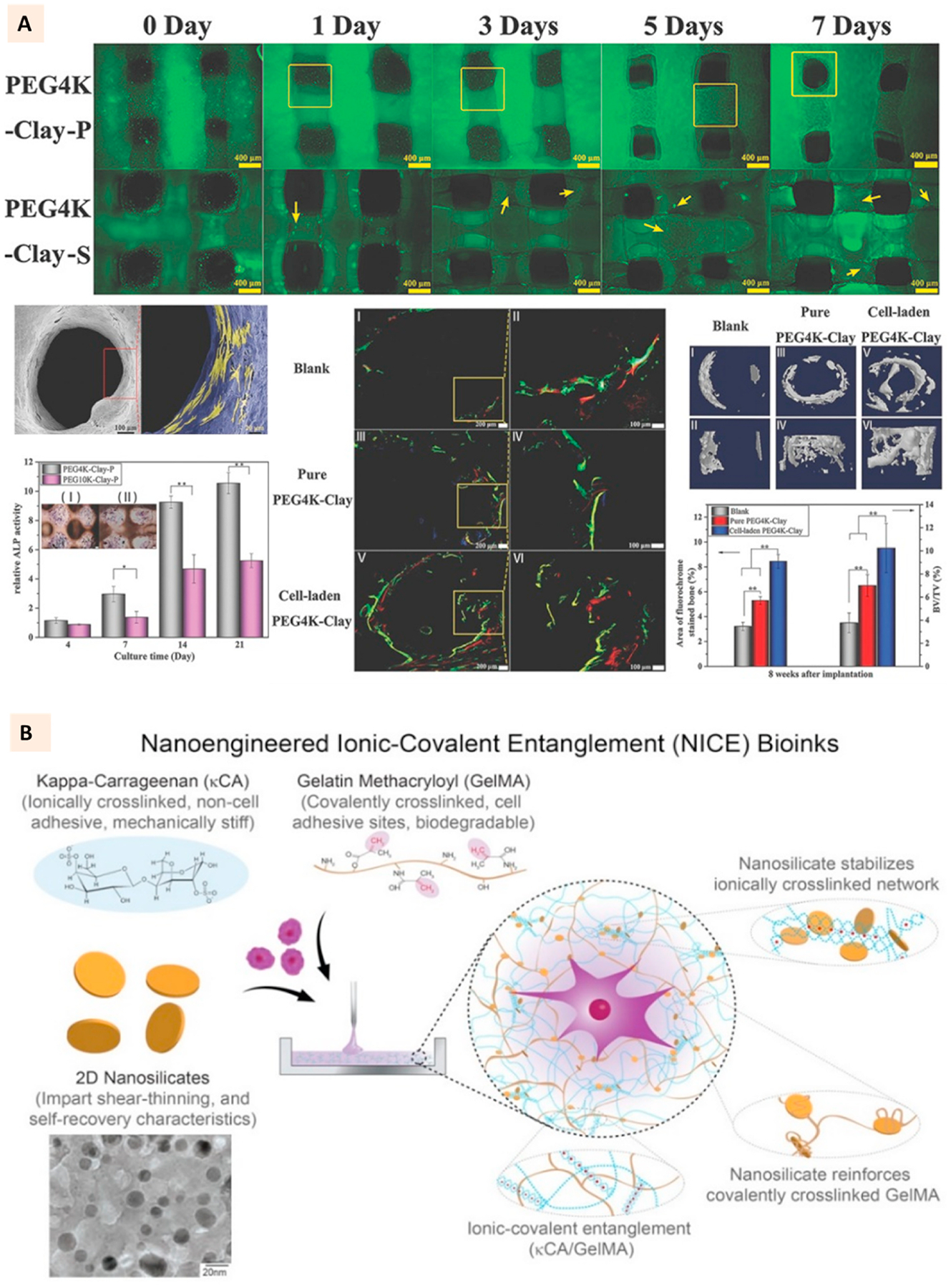
(A) Live/Dead cell assay for 3D bioprinted PEG-laponite constructs developed with two channel extrusion printing. One channel printed PEG-laponite and another channel deposited cells-hyaluronic acid laden in layer-by-layer fashion. SEM images showing the cell attachment to PEG-laponite scaffolds. Relative ALP activity and ALP stain (cross section) of PEG-laponite cell-laden constructs and the evaluation of in vivo bone formation with the cell-laden constructs in rat tibia model. (Adapted with permission from Ref. [108], Copyright 2017, John Wiley and Sons). (B) Constituents of NICE bioink where laponite is used to reinforce an ionic-covalent entanglement hydrogel developed with GelMa and kappa-carrageenan. TEM images show the uniform morphology of laponite particles. (Adapted with permission from Ref. [99], Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society).
