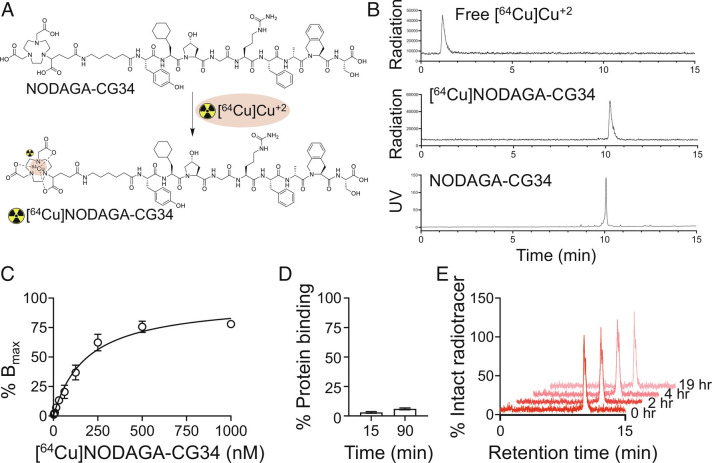
Fig. 1.
Radiolabeling of NODAGA-CG34 and select in vitro pharmacologic properties of [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34. (A) Radiolabeling of NODAGA-CG34 was performed by its incubation with [64Cu]CuCl2 in sodium acetate buffer containing gentisic acid at 40 °C for 30 min. (B) Radiolabeling efficiency >95% was consistently achieved as confirmed by radio-HPLC as a quality control threshold for proceeding to downstream experiments. Radio-HPLC of free [64Cu]Cu+2 (Top) has a retention time of ~1.2 min vs. [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34 (Middle) with a retention time of 10.2 min. Unlabeled NODAGA-CG34 (Lower) demonstrates a similar retention time by HPLC, as measured by UV detection, to that of [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34. (C) A saturation binding curve demonstrates specific (total minus non-specific) binding of [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34 to mCMKLR1 in HeLa cells transiently transfected with mCMKLR1 with a Kd of 192.1 ± 28.6 nM. Total and non-specific binding were conducted in the absence or presence of 2.5 µM Chem145-157, respectively. (D) The plasma protein binding of [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34 was determined by separation of bound and free [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34 using a size-exclusion column followed by γ-counting at specified timepoints. (E) Representative radio-HPLC chromatograms demonstrate high (~100%) in vitro stability of [64Cu]NODAGA-CG34 in mouse plasma at different time-points over a 19-h period. N = 3 independent experiments for all experiments, except for radiolabeling which has been performed >10 times. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.