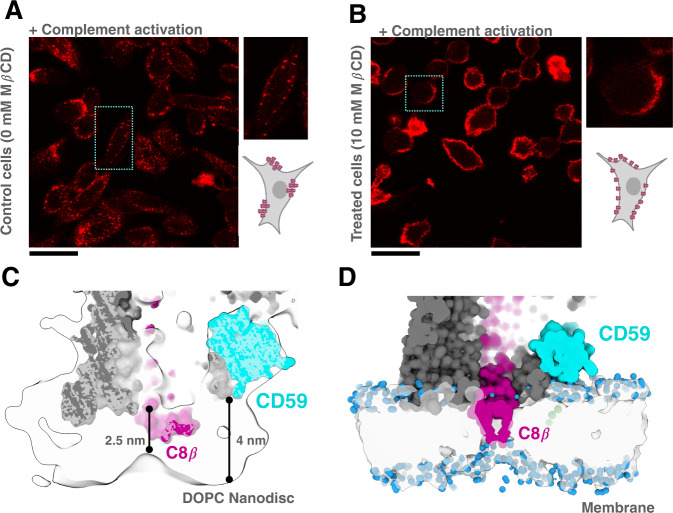
Fig. 5. Influence of the membrane environment on MAC assembly and inhibition.
A, B Cholesterol depletion assays. A representative image (out of 10 randomly selected locations) for each condition is shown. Scale bars, 50 μm. A Complement was activated on CHO cells with a polyclonal anti-CHO IgG antibody. Cells were incubated with C9-depleted human serum supplemented with a chemically labeled fluorescent C9 (C9-Alexafluor 568) capable of forming MAC. B CHO cells treated with MβCD to deplete cholesterol. Complement activation and C9 detection is as described in (A). Insets show a zoomed in view of single cell. Cartoon schematics highlight the pattern of MAC deposition. C CryoEM map of the C5b92-CD59 complex in a lipid nanodisc applying a positive B-factor of +50 Å2 (transparent surface). Surface rendering of the protein model is underlayed. CD59 is cyan, C8β is magenta and the remaining complement proteins are grey. D Map generated from the coarse-grained model of the C5b8-CD59 complex including the GPI anchor (green). Protein components colored as in panel (C). Water molecules in proximity to the membrane are shown as blue spheres. Initial and final configurations for the three MD repeats are included in the Supplementary Data Files.