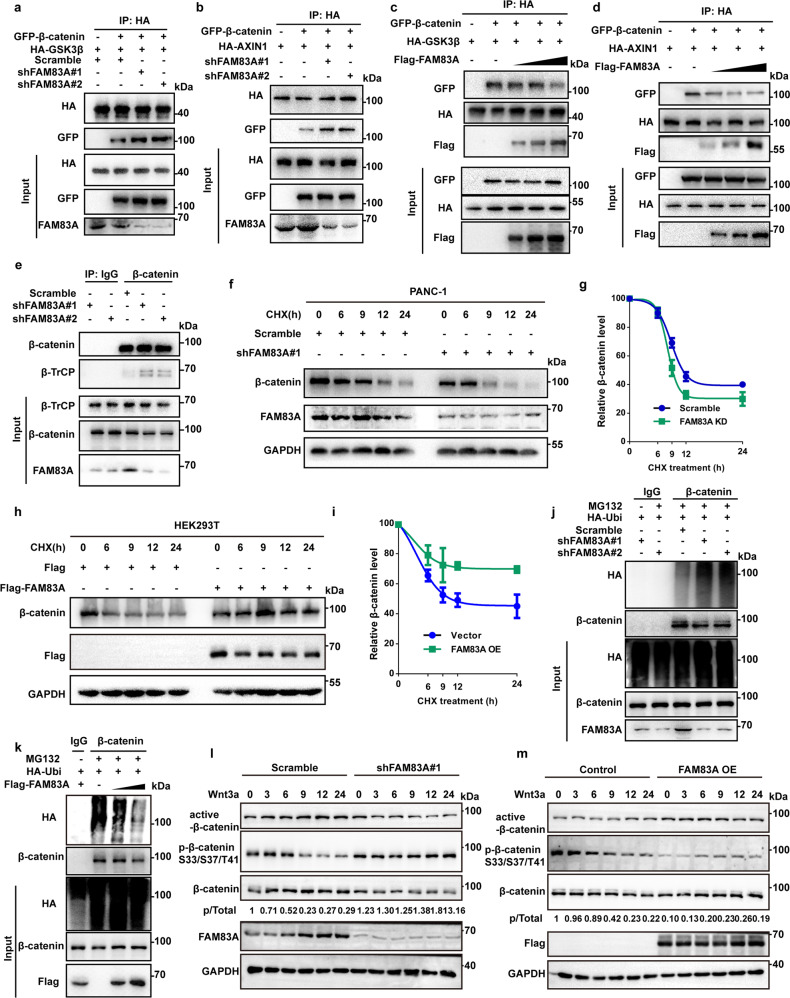
Fig. 3.
FAM83A inhibits the destruction complex formation and stabilizes β-catenin. a, b FAM83A knockdown using two specific small interfering RNAs (shFAM83A#1 and shFAM83A#2) enhanced the interaction between exogenous HA-tagged GSK3β, AXIN1 and GFP-tagged β-catenin in PANC-1 cell lysates. Protein interactions were analyzed by western blotting (n = 3). c, d The exogenous Flag-FAM83A dose-dependently decreased β-catenin-GSK3β and β-catenin-AXIN1 interactions in PANC-1 cell lysates. Protein interactions were analyzed by western blotting (n = 3). e FAM83A knockdown enhanced the interaction between endogenous β-TrCP and β-catenin in PANC-1 cell lysates. Protein interactions were analyzed by western blotting (n = 3). f, g FAM83A knockdown promoted the degradation of β-catenin protein upon cycloheximide (CHX, 20 μM) treatment for indicated times in PANC-1 cell lysates. Representative western blotting images and quantification data were shown (n = 3). h, i FAM83A overexpression inhibited the degradation of β-catenin protein upon cycloheximide (CHX, 20 μM) treatment for indicated times in PANC-1 cell lysates. Representative western blotting images and quantification data were shown (n = 3). j FAM83A knockdown increased the level of β-catenin ubiquitination upon MG132 (10 μM) treatment in PANC-1 cell lysates. Representative western blotting images were shown (n = 3). k FAM83A overexpression dose-dependently decreased the level of β-catenin ubiquitination upon MG132 (10 μM) treatment in PANC-1 cell lysates. Representative western blotting images were shown (n = 3). l, m Representative western blotting images of active-β-catenin, p-β-catenin S33/S37/T41 were shown after FAM83A knockdown or FAM83A overexpression upon Wnt3a (100 ng/mL) treatment for indicated times (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Data were presented as mean ± SD