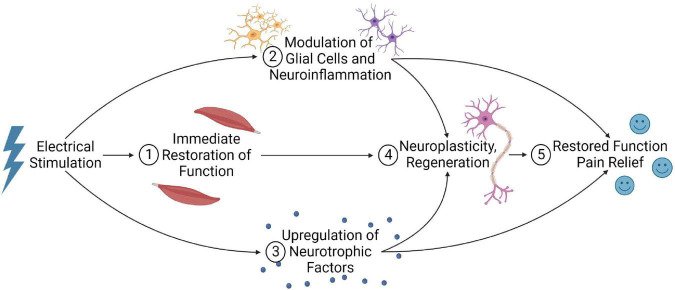
FIGURE 7.
Summary of the potential mechanisms that electrical stimulation may improve outcomes post-SCI. (1) Electrical stimulation can immediately restore function by activating local neural circuitry and facilitating spared, residual supraspinal inputs to regain functional control below the lesion. (2) Stimulation may also modulate glial cells and neuroinflammation, and (3) upregulate neurotrophic factors. (4) When combined with long-term stimulation and rehabilitation, this may promote neuroplastic remodeling of the spinal cord and possibly axonal regeneration, facilitating supraspinal control below the injury. (5) These mechanisms may account for the restored function and neuropathic pain relief observed in electrical stimulation studies.