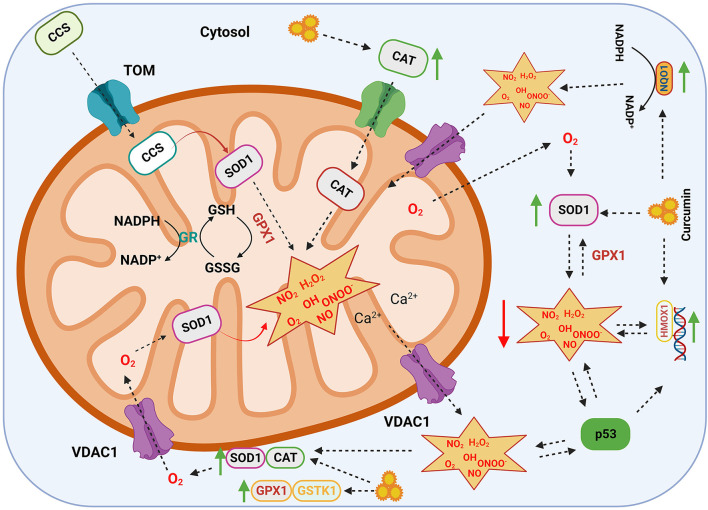
Figure 2.
Antioxidant mechanism of curcumin. Schematic diagram summarizing a network of antioxidant enzymes regulating the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are involved in a number of cellular reactions. Curcumin upregulates antioxidant enzymes such as GPX1, GSTK1, SOD1, CAT, NQO1, and HMOX1. The ROS present in the cytoplasm are transported to the mitochondrion through gatekeeper proteins such as VDAC1 where they are scavenged by antioxidant enzymes. SOD1, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; GPX1, glutathione peroxidase; GSTK1, glutathione-s-transferase kappa; HMOX1, heme oxygenase; NQO1, NAD (P) H quinone dehydrogenase; VDAC1, voltage-dependent anion channel; TP53, cellular tumor antigen p53; CCS, copper chaperone for SOD; GR, glutathione reductase; NO2, nitrogen dioxide; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; OH, hydroxyl radical; O2, superoxide; NO, nitric oxide; ONOO−, peroxynitrite. The green arrow represents upregulation and the red arrow represents downregulation.