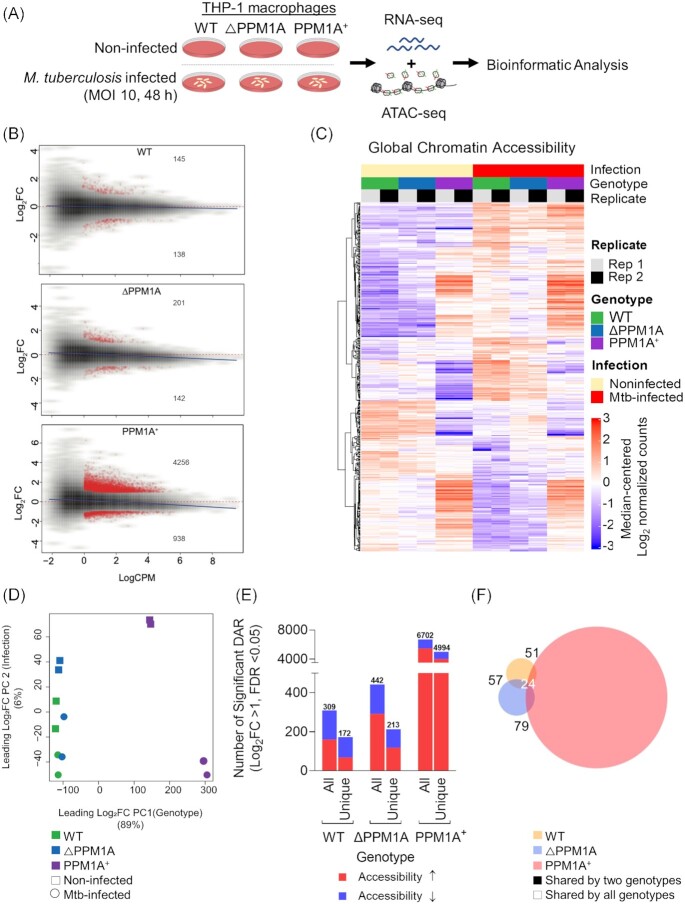
Figure 1.
Mtb infection induces global chromatin remodelling in macrophages. (A) Experimental schematic. WT, △PPM1A, and PPM1A+ THP-1 macrophages were infected with Mtb mc26206 at an MOI of 10 for 48 h. Then, Mtb-infected and noninfected control macrophages were harvested for ATAC-seq (two independent replicates) and RNA-seq (three independent replicates) in parallel from the same wells. (B) MA plots showing log2 fold-change versus average signal (log of counts per million, logCPM) in Mtb-infected samples compared to controls, in each of three genotypes studied. Peaks with significant chromatin accessibility changes are marked in red. Blue lines represent the general signal trend by loess fit. Red-dotted lines mark the location of identical signal. (C) Heatmap of chromatin accessibility in regions that were significantly differentially accessible in WT cells upon Mtb infection. Chromatin accessibility in WT, △PPM1A, and PPM1A+ macrophages before and after Mtb infection is shown. All ATAC-seq peaks were retained if they had >24 counts in at least two samples. Differential peaks between Mtb-infected WT macrophages and noninfected controls with absolute value of log2FC > 1 and FDR < 0.05 were considered significant. (D) PCA showing significant differential ATAC-peaks separate and cluster together based on the first and second principal components, which are genotype and Mtb infection status, respectively. Genotype accounts for 89% of the variance observed in all significant DAR, and Mtb infection accounts for 6%. (E) Total and unique DAR. The first bar displays the total number of all significant differential peaks in each genotype after Mtb infection, separated by whether chromatin accessibility increased or decreased. The second bar displays the total number of peaks that are unique to each genotype, separated by whether chromatin accessibility increased or decreased. (F) Venn diagram showing the overlap of significant differential peaks between Mtb-infected WT, △PPM1A, and PPM1A+ macrophages and noninfected macrophages.