Figure 2. Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters, dyspnoea, and supplemental oxygen use at baseline compared to 48 hours post-thrombectomy.
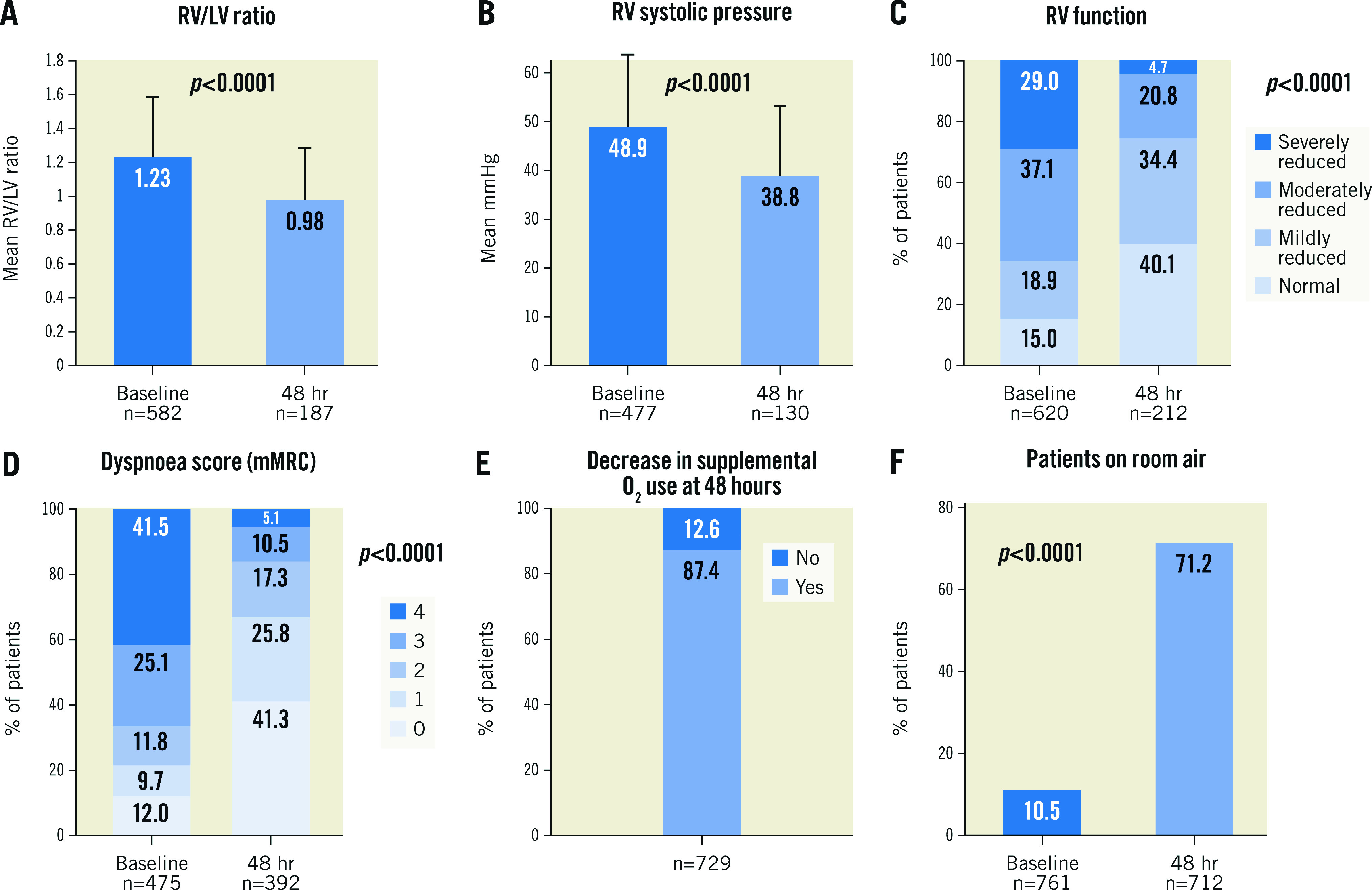
A) Change in RV/LV ratio (p<0.0001 for available paired assessments; McNemar’s test). B) Change in RV systolic pressure (p<0.0001 for available paired assessments; McNemar’s test). C) Change in the distribution of patients’ RV function (p<0.0001 for available paired assessments; McNemar-Bowker’s test). D) Dyspnoea was assessed at baseline and at 48 hours using the modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) assessment tool (higher score=worse dyspnoea). The proportion of patients with each score (0-4) is presented, showing a significant change in score distribution (p<0.0001 for available paired assessments; McNemar-Bowker’s test). E) The proportion of patients whose use of supplemental oxygen decreased from baseline to 48 hours is presented. A decrease was defined as a reduction in the oxygen volume used, or in the type of supplemental oxygen required (types of supplemental oxygen were ranked as a reduction if a patient moved from one type to another type in order as follows: intubation, face mask, nasal cannula, room air). F) The proportion of patients on room air at baseline and 48 hours post-thrombectomy is presented (p<0.0001 for paired assessments; McNemar’s test). hr: hours; LV: left ventricle; RV: right ventricle
