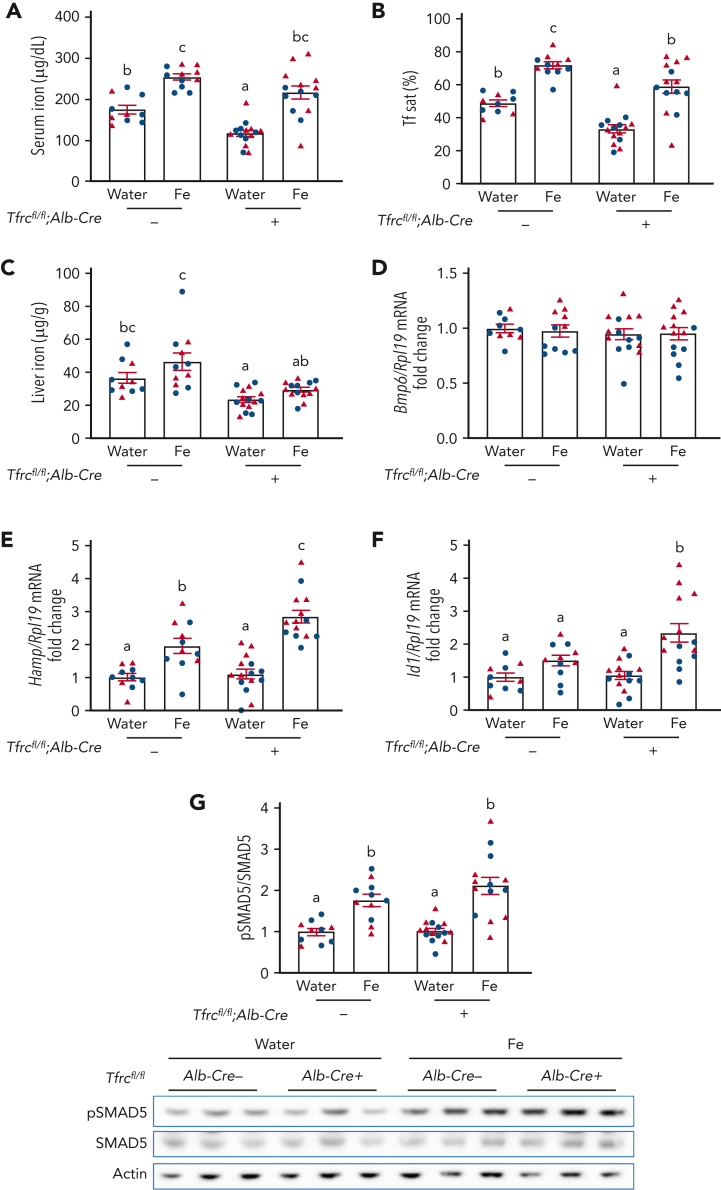
Figure 3.
Acute serum iron loading by oral gavage of iron induces higher hepcidin expression in Tfrcfl/fl;Alb-Cre+mice compared with Tfrcfl/fl;Alb-Cre−mice. Seven-week-old male (blue) and female (red) Tfrcfl/fl;Alb-Cre+ mice and littermate controls (Tfrcfl/fl;Alb-Cre−) were maintained on a low-iron diet (2-6 ppm iron). After 12 days, mice were orally gavaged with 2 mg/kg elemental iron (as ferrous sulfate) or distilled water. After 5 hours, (A) serum iron, (B) serum transferrin saturation, and (C) liver iron levels were analyzed by colorimetric assays. Livers were analyzed for (D) Bmp6, (E) Hamp, and (F) Id1 relative to Rpl19 mRNA by qRT-PCR. (G) Liver pSMAD5 relative to total SMAD5 and actin protein were analyzed by immunoblot and chemiluminescence quantitation. A representative immunoblot is shown. For panels D-G, the average of the water-treated control mice was set to 1. For all graphs, individual data points are shown, and bars represent mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance with Tukey post hoc test. Means without a common superscript differ significantly (P < .05). qRT, quantitative reverse transcription; SEM, standard error of the mean.