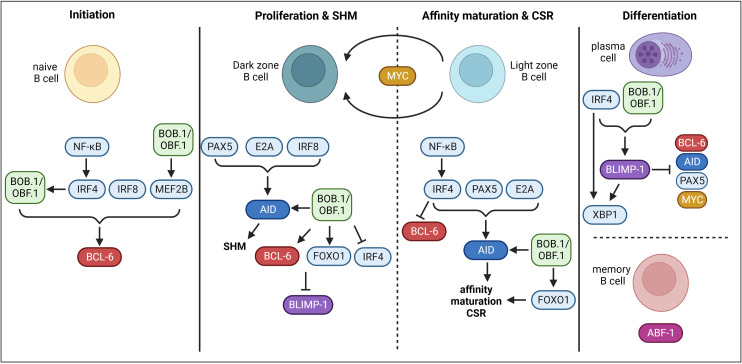
Figure 1.
Transcriptional control of GC B cells. During GC initiation, TFs IRF4, IRF8 and MEF2B induce the expression of BCL-6. BOB.1/OBF.1 is also involved in the initiation of BCL-6 expression. Moreover, the transcriptional co-activator drives MEF2B expression. On the other hand, IRF4 seems to modulate the expression of BOB.1/OBF.1. In the dark zone, PAX5, E2A and IRF8 induce AID and therefore SHM. BOB.1/OBF.1 was also shown to be involved in AID, BCL-6 and FOXO1 induction. BCL-6 and FOXO1 inhibit BLIMP-1 and BOB.1/OBF.1 blocks IRF4 expression to prevent initiation of plasma cell differentiation at this stage. In the light zone, IRF4 is upregulated and prevents BCL-6 expression to terminate the dark zone program. IRF4, PAX5 and E2A promote AID expression and thereby affinity maturation and CSR. BOB.1/OBF.1 (POU2AF1) is again involved in regulation of AID and FOXO1 expression. The TF MYC probably regulates re-entry into the dark zone. IRF4 and BOB.1/OBF.1 are involved in driving BLIMP-1 expression. BLIMP-1 in turn represses BCL-6, AID, PAX5 and MYC and on the other hand facilitates expression of XBP1 together with IRF4 resulting in plasma cell differentiation. In contrast, ABF-1 induces memory B cell differentiation. This figure was created with BioRender.com.