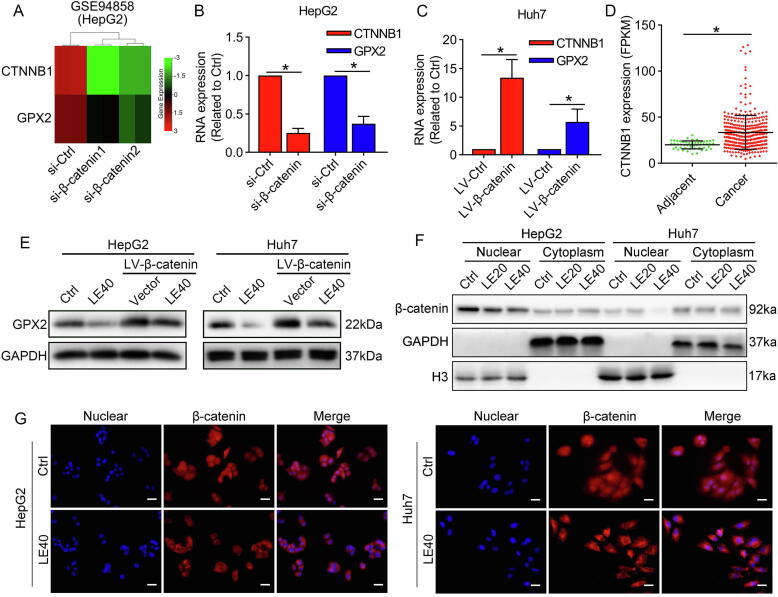
Fig. 4.
Lenvatinib regulate β-catenin/GPX2 axis in HCC cells. (A) Analyses of GEO database (GSE94858) showed that specific siRNA of β-catenin marked suppressed CTNNB1 expression. (B–C) Our results further confirmed that GPX2 expression was markedly inhibited by si-β-catenin in HepG2 cells, while upregulated β-catenin increased GPX2 expression in Huh7 cells. (D) Analyses of the TCGA database showed that CTNNB1 was significantly overexpressed in HCC tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. (E) The western blot results revealed that lenvatinib inhibited GPX2 expression through modulating β-catenin. (F) The nuclear and cytoplasm proteins were collected for western blot analysis. The results showed that β-catenin levels in the nuclear were marked decreased after the treatment of lenvatinib in both HepG2 and Huh7 cells. (G) Immunofluorescence detection demonstrated that lenvatinib could prevent the nuclear translocation of β-catenin in HepG2 and Huh7 cells. Scale bars: 40 μm. Data represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical evaluation of the data was assessed using Student’s t-test (B-D). P > 0.05, ns: no significance.