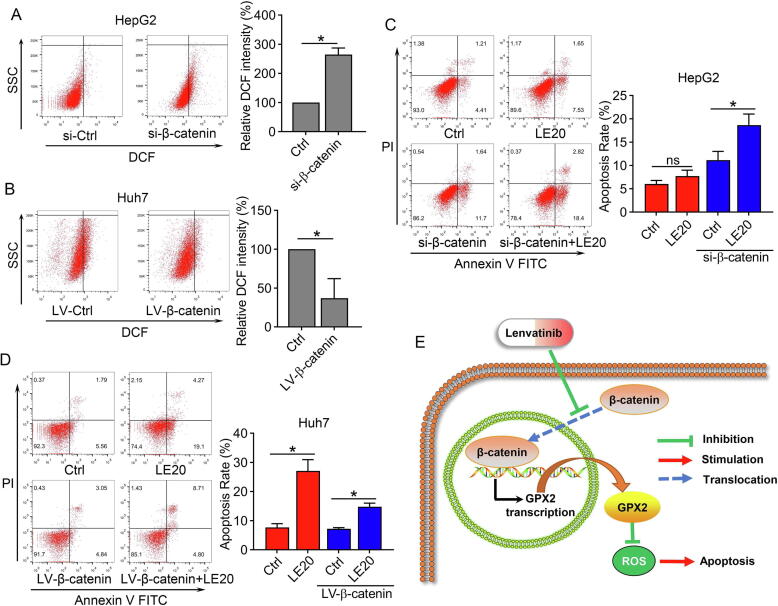
Fig. 5.
β-catenin regulated ROS levels and decreased lenvatinib sensitivity in HCC cells. (A–B) Flow cytometry results demonstrated that si-β-catenin could increase ROS levels in HepG2 cells, while LV-β-catenin could decrease ROS levels in Huh7 cells. (C) Flow cytometry results revealed that lenvatinib at the dose of 20 μmol/L had limited effect on cell apoptosis in HepG2 cells, while down-regulation of β-catenin marked enhanced the anti-tumor effect of lenvatinib against HepG2 cells. (D) The results demonstrated that overexpression of β-catenin impaired the anti-tumor effect of lenvatinib against Huh7 cells. (E) Illustrative model showed the proposed mechanism that lenvatinib induced ROS related apoptosis by regulating the β-catenin/GPX2 axis. Statistical evaluation of the data was assessed using Student’s t-test (A-B) and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni correction (C–D). *P < 0.05; P > 0.05, ns: no significance.