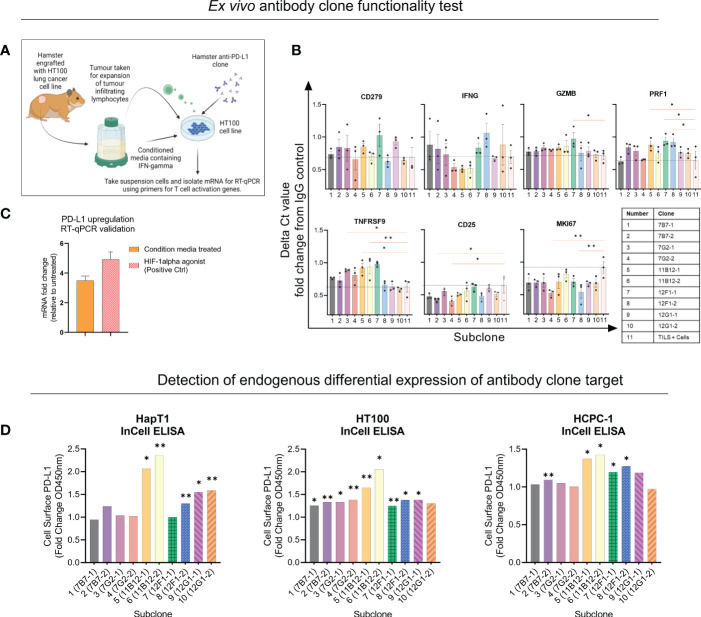
Figure 2.
Selection of anti-Syrian hamster PD-L1 subclones by in vitro functionality. (A) Illustration of co-culture experiment design. (B) Seven T cell activation genes were measured from suspension cells isolated from the anti-PD-L1 subclone co-culture as measured by RT-qPCR. Values are presented as fold change from IgG control and the black dotted horizontal line represents the ‘baseline’ of HT100 + TILs without subclone. (C) Validating upregulation of endogenous PD-L1 on HaPT1 by RT-qPCR following exposure to conditioned media with a HIF-1 agonist as a positive control. (D) Detection of endogenous differential PD-L1 expression on the surface of three Syrian hamster cancer cell lines by anti-PD-L1 subclones as measured by In-Cell ELISA. Diluted conditioned media was used to upregulate PD-L1 and was compared to untreated control. PD-L1+ signal was measured by absorbance OD450 of HRP-conjugated antibody detecting mouse IgG. Clones able to detect differential expression of PD-L1 were considered more specific for PD-L1 detection. The absorbance values were normalized to cell number as measured by Janus Green Whole-Cell Stain. Data and error bars are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.