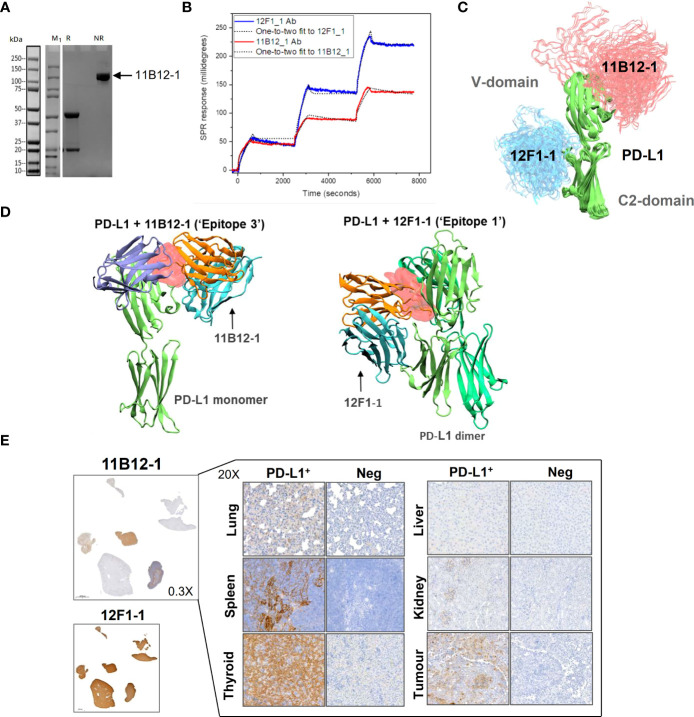
Figure 4.
Analysis of anti-PD-L1 mAb binding characteristics supports 11B12-1 as a therapeutic antibody. (A) Molecular weight analysis of 11B12-1 by SDS-PAGE where M1 indicates protein ladder, R: reducing conditions and NR: non-reducing conditions. Purified 11B12-1 is indicated by the arrow under non-reducing conditions (~100kDa). (B) Sensorgrams of binding affinities of 11B12-1 and 12F1-1 with PD-L1 analyzed by surface plasmon resonance binding assay. (C) Snapshots of antibody-antigen complex generated by AF2/ColabFold. For each antibody 20 models from 4 independent runs are overlaid. 11B12-1 is shown in red, 12F1-1 in blue, PD-L1 is depicted in green color. All structures are aligned with respect to PD-L1 coordinates. (D) Upper: 11B12-1 clashes with ligand PD-1 (ice-blue). Lower: 12F1-1 clashes with PD-L1 dimer (lime & green). Steric clashes (0.3 nm cutoff) are marked as red surface. Antibody VL chain is shown in orange and VH chain in cyan. (E) Immunohistochemistry staining of Syrian hamster organs with 11B12-1 and 12F1-1. Antibody clone 11B12-1 is expanded into higher magnification (20X) for each hamster organ, whereas 12F1-1 was not because of non-specific staining.