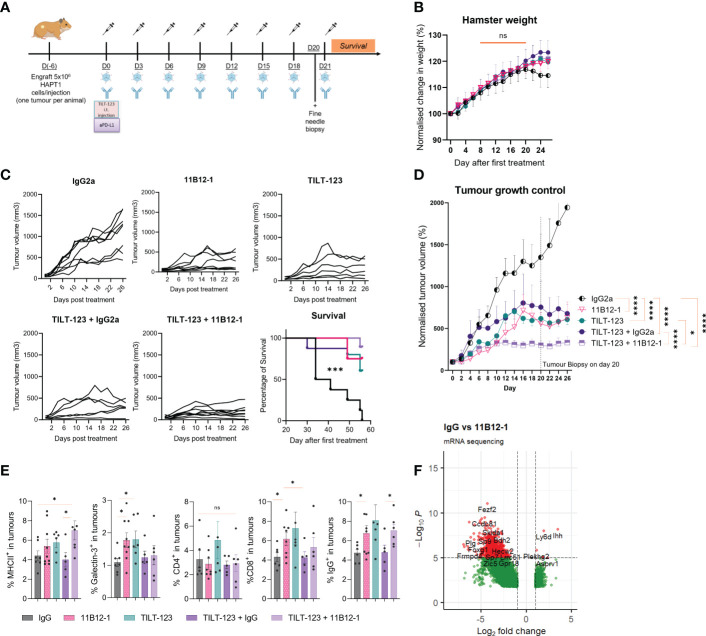
Figure 5.
Combination therapy with 11B12-1 and oncolytic adenovirus Ad5/3-E2F-D24-hTNFα-IRES-hIL-2 provides superior tumour growth control in a Syrian hamster model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. (A) Schematic of treatment scheme. HapT1 (heterotopic PDAC) bearing Syrian hamsters (n=8 per group) were intraperitoneally injected with 11B12-1 (300 µg) or isotype control (300 µg) and with or without intratumoural injection of 1x108 VPs of Ad5/3-E2F-D24-hTNFα-IRES-hIL-2. Treatments were given every three days for a total of 8 treatments. Fine needle tumour biopsies were taken on the day before the last treatment for evaluation of mechanism of action. (B) Percentage change in weight of hamsters after treatments. Data is normalized to day 0. (C) Individual tumour growth curves with 60 day survival analysis. (D) Mean percentage change in tumour volume over 28 days. (E) Phenotypic analysis of intratumoural immune cells in fine needle aspirates by flow cytometry. (F) Volcano plot for significantly differentially expressed genes between IgG2a and anti-PD-L1 clone 11B12-1. DESeq2 was used to compare gene expression between groups and the Wald test was used to generate p-values and log2 fold changes. Genes with an adjusted p-value < 0.05 and absolute log2 fold change > 1 were determined as differentially expressed genes. Significance for tumour growth controls was calculated using two-way mixed model ANOVA and survival curves by Mantel–Cox log-rank test. Statistical significance of flow cytometry data was evaluated using an unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 ns not significant. All data and error bars are presented as mean ± SEM.