Figure 1 |.
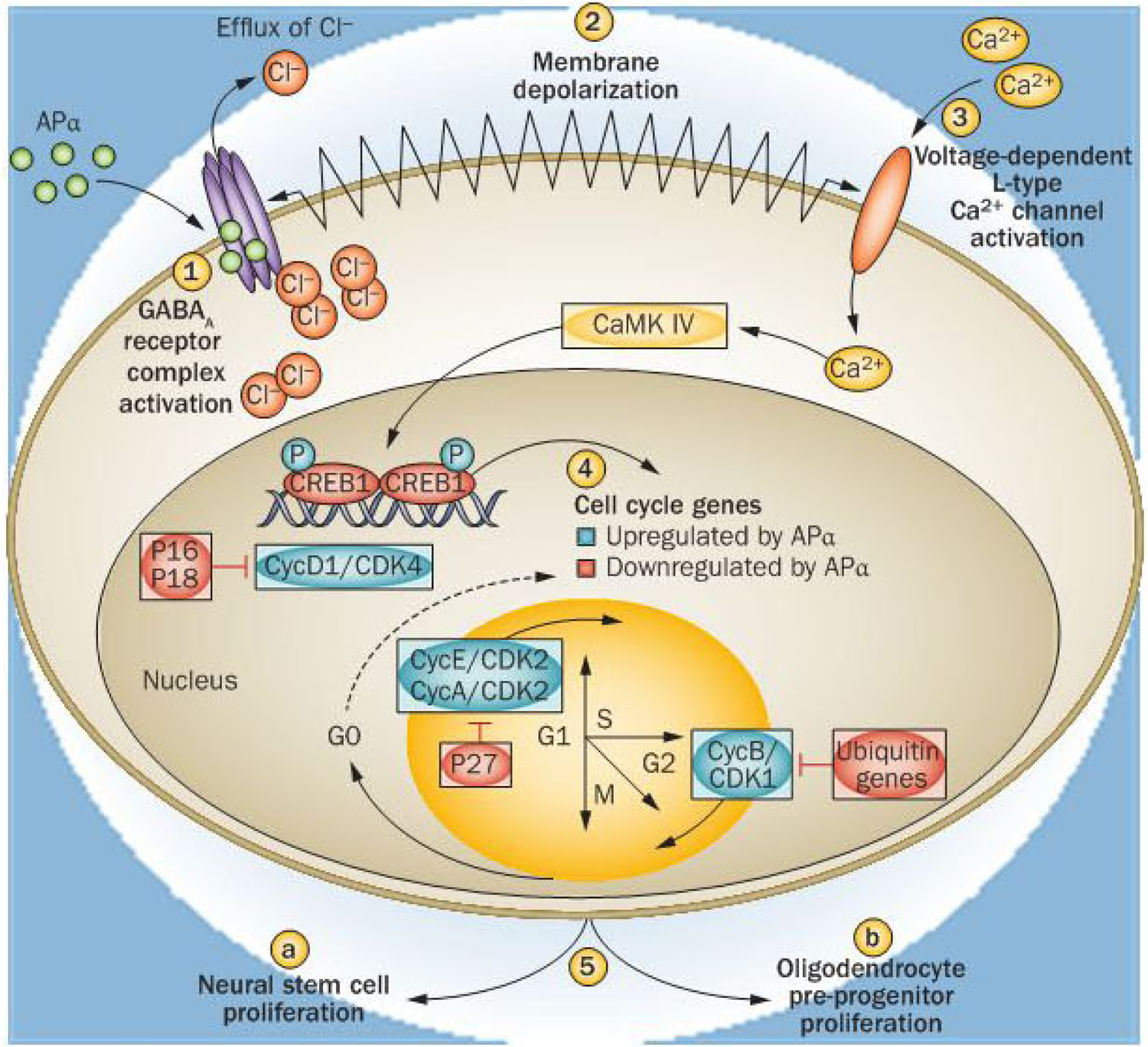
Mechanism of allopregnanolone-induced neural stem cell and oligodendrocyte precursor progenitor mitosis. Allopregnanolone (APα) binds to sites within the transmembrane domains of the GABAA receptor complex to both potentiate and directly activate the GABAA receptor complex (1). APα potentiates GABAA receptor complex responses through binding in a cavity formed by the α-subunit transmembrane domains, whereas direct receptor activation occurs through binding at the interface between the α and β subunits and is enhanced by APα binding to the potentiation site.74 Owing to expression of the SLC12A2 cotransporter in neural stem cells, intracellular Cl− is elevated relative to extracellular Cl−, such that activation of the GABAa receptor complex leads to an efflux of Ch. Efflux of Cl− from the intracellular compartment leads to membrane depolarization (2). Efflux of negatively charged ions leads to membrane depolarization and activation of voltage-dependent L-type calcium (Ca2+) channels β). The subsequent rise in intracellular Ca2+ activates a Ca2+-dependent kinase, CaMK IV, which then phosphorylates and activates the transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (CREB1). Through CREB1 activation, APα upregulates expression of cell cycle genes required for transition from GO to S and M phases of the cell cycle (4).22 Simultaneously, genes that express proteins that repress cell division, such as the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors P16 and P18 and ubiquitins, are downregulated.22 Successful transition through the cell cycle leads to neural stem cell proliferation in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus and oligodendrocyte precursor progenitors in white matter (5). The mechanism of APα-induced neurogenesis takes advantage of the developmentally regulated Cl− gradient to activate a Ca2+-to-CREB signalling cascade to induce mitosis in those cells phenotypically competent to divide whilst not activating this pathway in mature neurons.22,75 Abbreviations: Ca2+, calcium; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; Cl−, chloride; Cyc, cyclin; Ub, ubiquitin.
