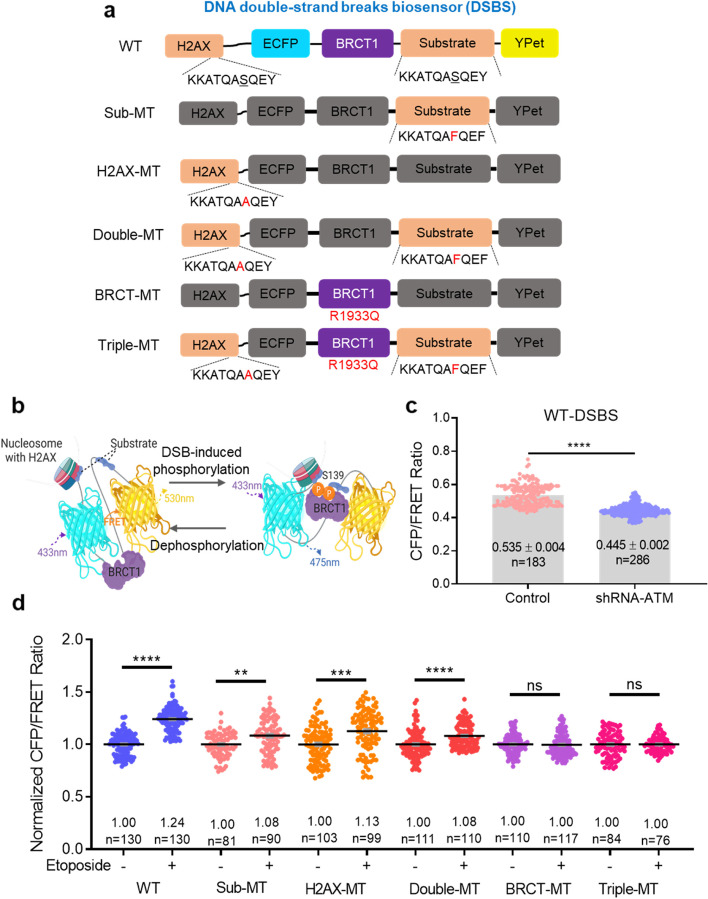
Fig. 1.
Design and characterization of the FRET-based DNA double-strand breaks biosensors (DSBS). a Schematic diagram of the DSBS. The DSBS is composed of full-length H2AX, an ECFP donor, BRCT1 domain derived MDC1, a substrate of partial H2AX, and an YPet acceptor. The fragments of DSBS mutants are the substrate (S139A, Sub-MT), full-length H2AX (S139F, H2AX-MT), two Ser139 phospho-peptides (Double-MT), BRCT1 (R1933Q, BRCT-MT), and the previous three residues (Triple-MT). b The WT-DSBS shows the conformational change by interacting between DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs)-induced phospho-Ser139 and the BRCT1 domain, leading to a decrease in the FRET. Conversely, dephosphorylation induces an increase in the FRET. This diagram was produced by BioRender (http://biorender.com/). c The CFP/FRET ratios of WT-DSBS in HEK293T cells transfected with control or shRNA-ATM, (5′-GATCCCCGGATTTGCGTATTACTCAGTTCAAGAGACTGAGTAATACGCAAATCCTTTTTGGAAA-3′ (sense)). d The normalized CFP/FRET ratios of WT-DSBS and mutants in HEK293T cells treated with 100 µM etoposide for 1 h (not significant (ns), **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001)