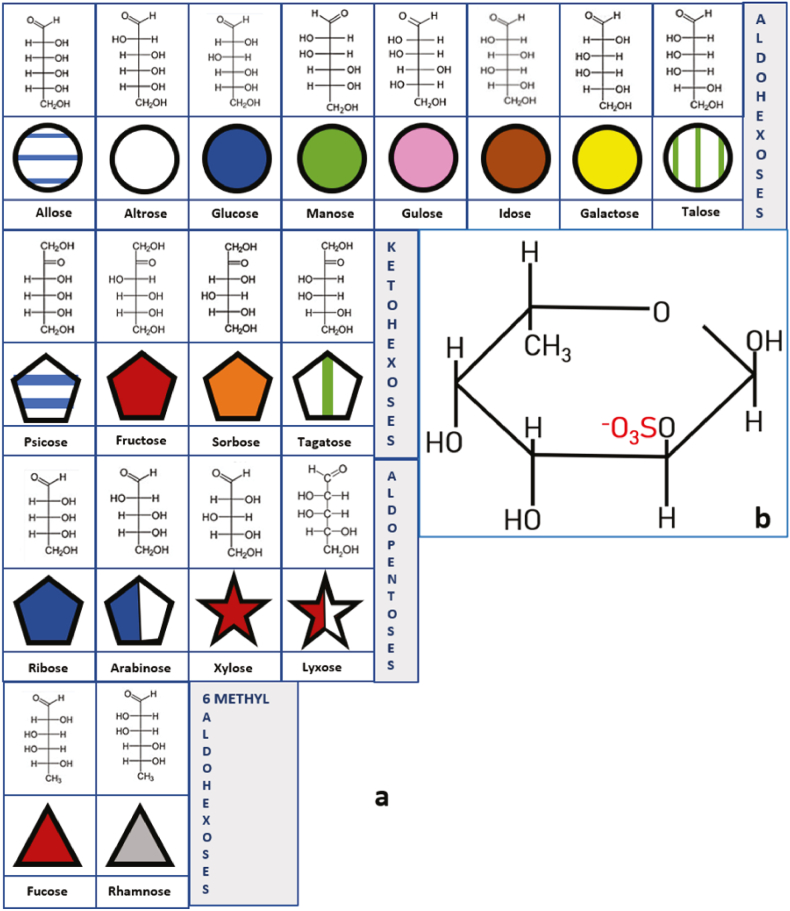
Fig. 1.
Fisher structure, symbolic representations of most common sugars prone to be sulfated. From upper to lower rows: a. Aldohexoses: six-carbon sugars with an aldehyde group that reacts with the OH group of C6 to form an intramolecular hemiacetal; Ketohexoses: six-carbon sugars with a keto group that can react with the OH group of C6 or C5 to form an intramolecular hemiketal; Aldopentoses: five-carbon sugars with an aldehyde group that reacts to form an intramolecular hemiacetal; and, 6-methyl-aldohexoses: six-carbon sugars with an aldehyde group that reacts to form an intramolecular hemiacetal with the alcohol group of C5. Carbon 6 forms a methyl group. b. One example of sulfation in a Fucose 2 sulfate molecule. OH groups are prone to be esterified with SO3− groups. In the case of fucose there are four potential sulfation sites. Modified from Ref. [8].