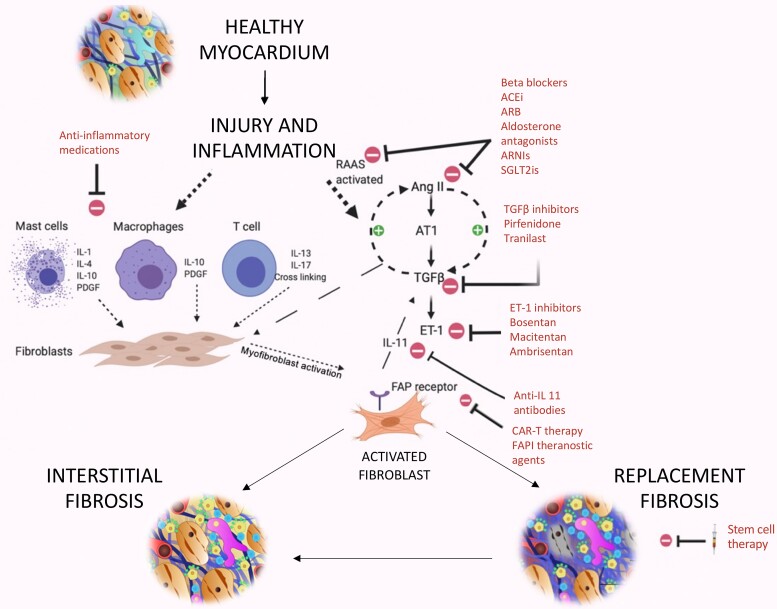
Figure 4.
Potential therapeutic targets in myocardial fibrosis. Relevant pathways involved in fibrosis formation include Angiotensin-II, transforming growth factor-β, and interleukin-11 making them key treatment targets. Other targets include the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, sympathetic and immune systems, endothelin 1, stem cell therapy, CAR-T therapy, and theranostic FAP inhibitor agents. AngII, angiotensin-II; ACE-i, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor; AT1, Angiotensin receptor; CAR-T, chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells; ET-1, endothelin-1; FAPI, fibroblast activation protein inhibitor; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; IL, interleukin; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor (beta).