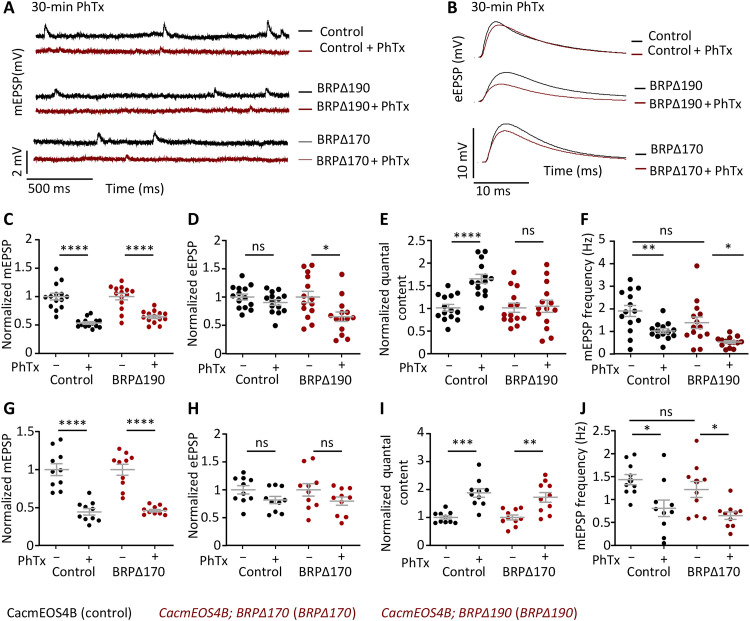
Fig. 8. Electrophysiological characterization of BRP∆170 and BRP∆190 mutants in CacmEOS4B background at normal or 30-min PhTx-treated remodeling AZs.
(A to I) Electrophysiological recordings of CacmEOS4B (Con), CacmEOS4B;BRP∆170/brp69 (BRP∆170), and CacmEOS4B;BRP∆190/brp69 (BRP∆190) mutants in CacmEOS4B (Con) background. Electrophysiological recordings of Con, BRP∆170, and BRP∆190 animals after 30-min incubation in HL3 or 50 μM PhTx in HL3 solution using current-clamp recordings. Representative traces of mEPSP and eEPSP in Control, BRP∆190, and BRP∆170 (A and B) animal before (− PhTx; black line) and after 30 min of PhTx (+ PhTx; red line) treatment. Scale bars, 10 mV and 10 ms (eEPSP); 2 mV and 500 ms (mEPSP). Quantifications of mEPSP amplitude, eEPSP amplitude, quantal content, and mEPSP frequency in PhTx-treated, untreated Control, and BRP∆190 (C to F) or BRP∆170 (G to J) mutant cells are normalized on the measurement obtained without PhTx for each genotype. Measurements were performed at third-instar larval muscle 6 NMJs of abdominal segments 2 and 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.