Figure 1.
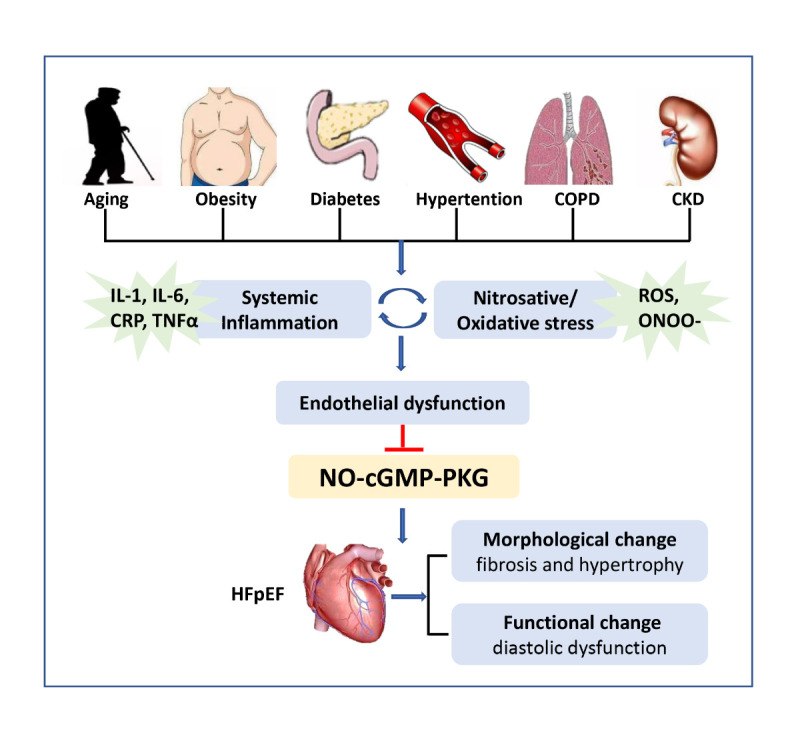
Impaired NO-cGMP-PKG axis in HFpEF. Risk factors for ageing and common comorbidities (including obesity, diabetes, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease) drive systemic inflammation, which further activates coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation and nitrosation/oxidative stress. The vicious cycle between inflammation and nitrosation/oxidative stress contributes to endothelial dysfunction, which further disrupts the signalling communication between endothelial cells and other types of cells in the heart. The suppression of NO-cGMP-PKG signalling in HFpEF ultimately results in cardiac structural changes and functional damage. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CKD: chronic kidney disease, IL-1: interleukin-1, IL-6: interleukin-6, CRP: C-reactive protein, TNFα: tumour necrosis factor α, ROS: reactive oxygen species, ONOO-: peroxynitrite, NO: nitric oxide, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, PKG: protein kinase G, HFpEF: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
