Figure 3. Cross-validation of in vitro and in vivo models facilitates investigations into joint disease mechanisms and the development of potential treatments.
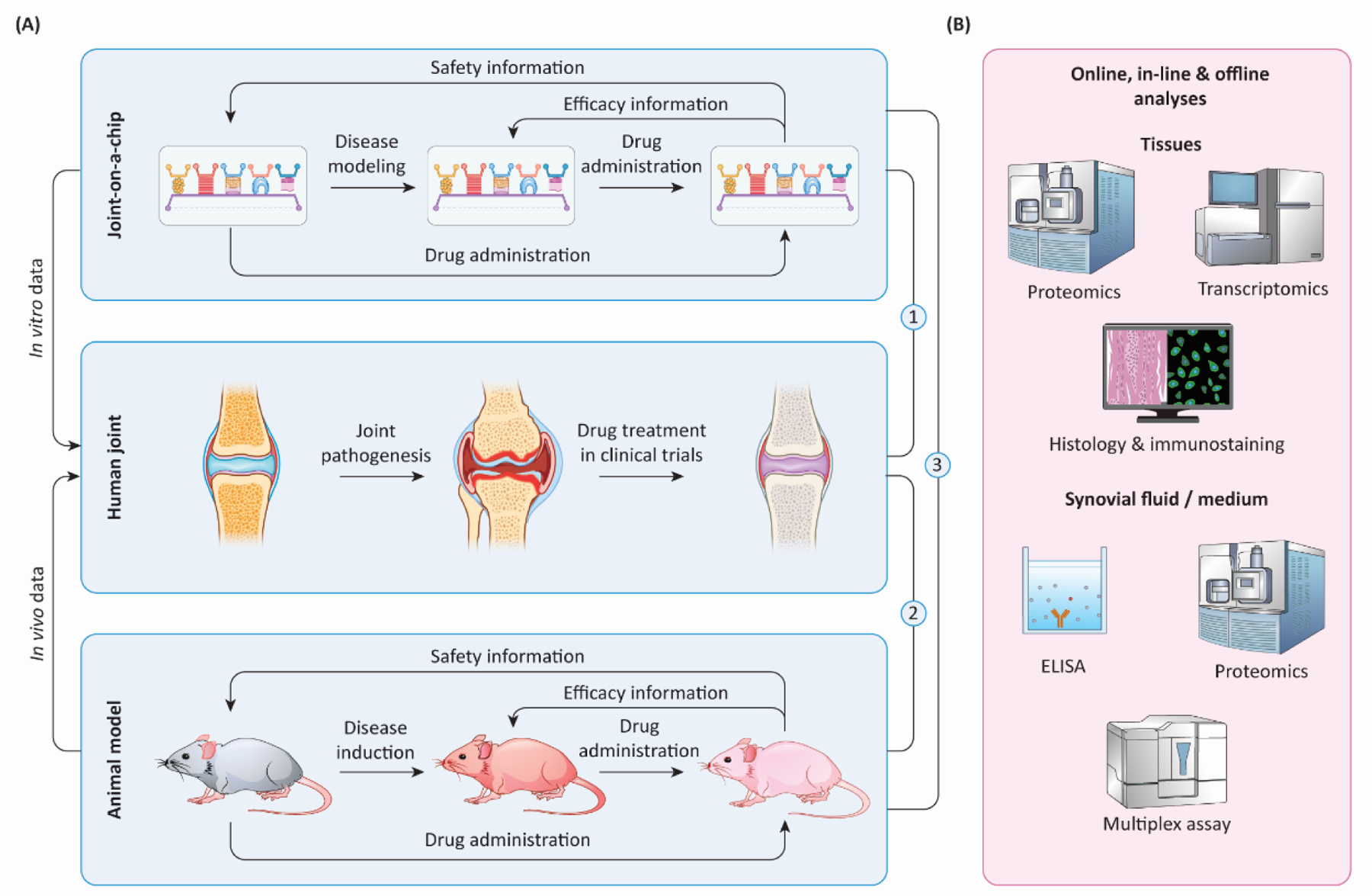
(A) Through simulating different aspects of arthritis in humans, both joint-on-a-chip (in vitro) and animal models (in vivo) provide valuable information on predicting drug safety and efficacy in humans. Before joint-on-a-chip can be used as a preclinical model, cross-check of treatment outcomes from three systems, indicated by ① ② ③, with clinically tested drugs, is essential. (B) To define the fidelity of joint-on-a-chip and animal models in simulating human arthritis and response to treatments, harvested tissues and fluids can be analyzed with different methods. ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
