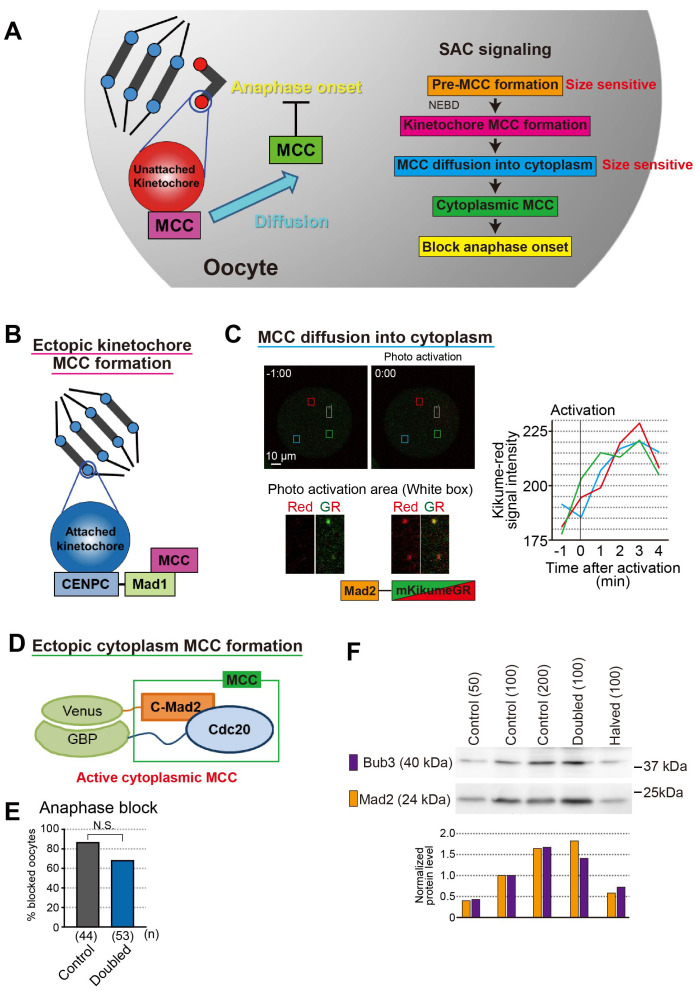
Fig. 4.
Spindle assembly checkpoint in oocyte. A. SAC signal pathway. Pre-MCC formation and MCC diffusion into cytoplasm step size sensitive. B. Ectopic kinetochore MCC formation by tethering Mad1 to kinetochore. C. Kinetochore Mad2 diffusion rate was fast and spread uniformly. Mad2-kikumeGR was expressed in oocytes. After activation few kinetochore (white box area), kikume-red signal intensity was measured at three different points (red, blue, and green box areas). The graph showed signal intensities were increased within 3 minutes and increasing rates were same among three different area. D. Ectopic cytoplasm MCC formation by inducing dimerization of C-Mad2 and Cdc20 in the cytoplasm [86]. E. Anaphase block by ectopic cytoplasm MCC formation in control and doubled oocytes. Bar graph shows the percentages of metaphase-arrested oocytes 10.5 h after NEBD. Chi-square tests were performed. N.S., not significant. F. Bub3 and Mad2 protein levels in halved and doubled oocytes. Western blotting analysis was performed and analysis the protein level of Bub3 and Mad2. The protein levels of Bub3 and Mad2 depended on their cytoplasmic amount, suggesting that their concentrations in the cytoplasm were almost constant. The number of oocytes loaded is indicated in parentheses.