FIGURE 4.
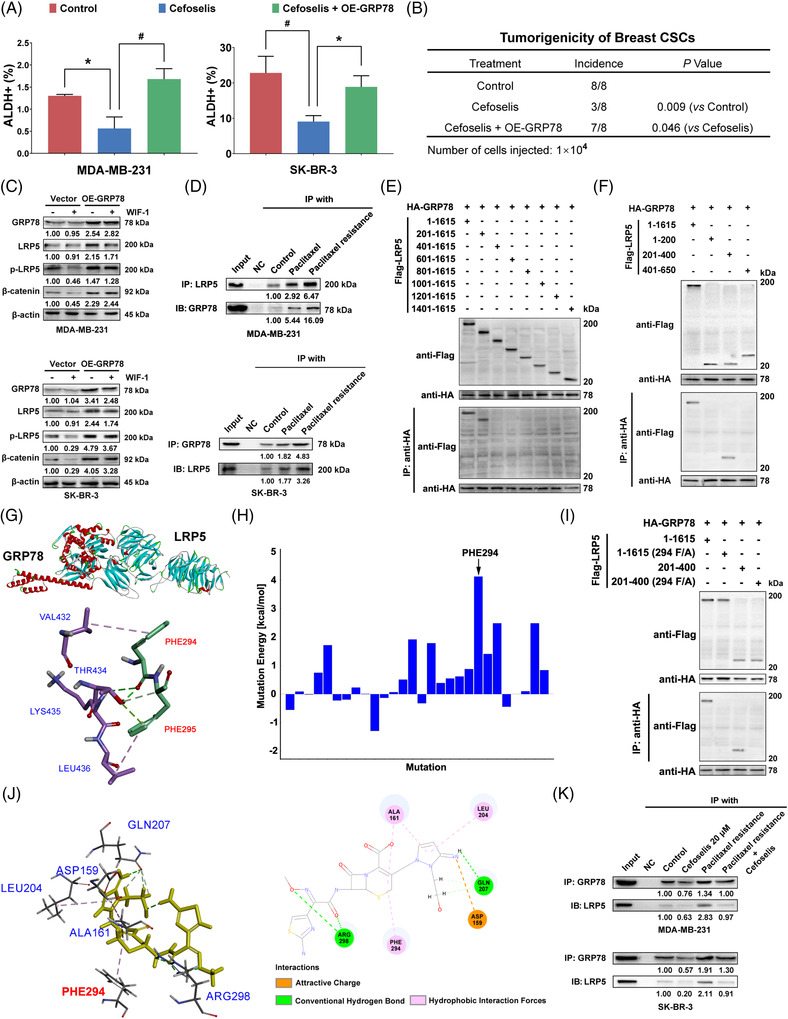
Cefoselis disrupts the interaction between GRP78 and LRP5 via PHE294. (A) ALDH+ frequency of breast cancer cells with GRP78 overexpression was detected following cefoselis (20 μM) treatment. (B) The CD44+/CD24−/low subpopulation of control or GRP78 overexpressing SK‐BR‐3 cells was sorted and inoculated into the mammary fat pads of NOD/SCID mice at the density of 1×10. 4 The tumour incidence was identified and compared following cefoselis (25 mg/kg) treatment (n = 8). (C) β‐catenin, LRP5 and its phosphorylation levels were measured in MDA‐MB‐231 and SK‐BR‐3 cell lines following GRP78 overexpression under the administration of Wnt inhibitor WIF‐1 (1 μg/ml) for 24 h. (D) The interaction of GRP78 with LRP5 was analysed in paclitaxel‐resistant and paclitaxel‐treated (24 nM) MDA‐MB‐231 and SK‐BR‐3 cells by Co‐IP assays. (E) The full length of LRP5 amino acids was truncated into every 200 fragments and labelled with a Flag to coprecipitate with HA‐labelled GRP78. The successful construction of the recombinant plasmids was verified by western blot using anti‐Flag and anti‐HA antibodies. Co‐IP was then performed using anti‐HA coupled resin. (F) The LRP5 fragments, including 1–200, 201–400, and 401–650, were synthesised to coprecipitate with HA‐labelled GRP78 to confirm the binding sites. (G) The binding mode between GRP78 and LRP5 was performed by molecular docking analysis. (H) The mutation energy was estimated if the binding site was mutated. (I) Co‐IP analysis was performed to verify the interaction between GRP78 and LRP5 when PHE294 of LRP5 was mutated to alanine. (J) The interaction forces, sites, and types between cefoselis and LRP5 were analysed by molecular docking. (K) The interaction of GRP78 with LRP5 was analysed in MDA‐MB‐231 and SK‐BR‐3 cells following cefoselis (20 μM) treatment. Their interactions in the paclitaxel‐resistant cells were also analysed following cefoselis administration. Data were represented as mean ± SD. For statistical analysis, one‐way ANOVA and Bonferroni as post hoc test (A) and Wilcoxon test (B) were applied. * p < .05, # p < .01. OE‐GRP78: GRP78 overexpression
