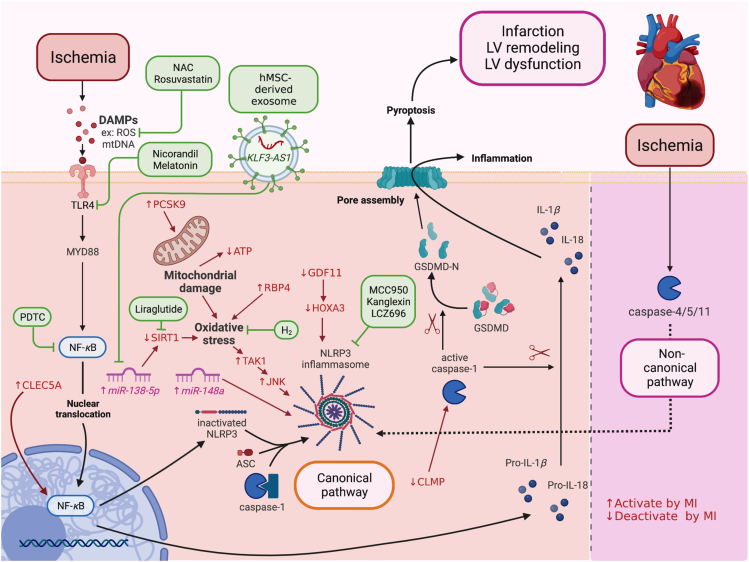
Figure 1.
The canonical and non-canonical pathways of MI-induced pyroptosis and potential interventions. DAMPs such as ROS, mtDNA bind to TLR4 and activate MYD88/NF-κB/ASC/caspase-1/NLRP3 pathways in the canonical pathway. In the non-canonical pathway, MI activates caspase-4/5/11 and NLRP3 signaling. After the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, caspase-1 becomes active caspase-1, which cleaves pro-IL-1β to IL-1β, pro-IL-18 to IL-18, GSDMD to GSDMD-N. GSDMD-N then forms pores in the plasma membrane, causing pyroptotic cell death and secretion of IL-1β, IL-18 to cause more inflammation. NAC, rosuvastatin, nicorandil, melatonin, PDTC, lncRNA KLF3-AS1, liraglutide, H2, MCC950, kanglexin, and LCZ696 reduce cardiomyocyte/myocardial damage against MI by targeting the canonical pathway of pyroptosis, leading to the reduction of GSDMD. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; GSDMD, Gasdermin D; GSDMD-N, Gasdermin D N-terminal fragment; IL, interleukin; lnc-RNA, long non-coding ribonucleic acid; MI, myocardial infarction; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; MYD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3; PDTC, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4.