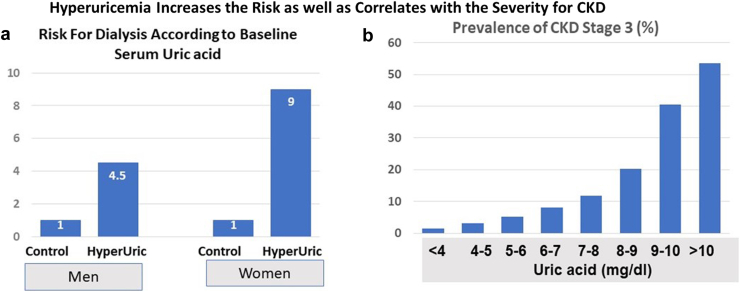
Figure 1.
Relationship of Serum Uric acid with CKD. (a) A study in which more than 48,000 Japanese that were 20 years or older who were followed for 7 years. After controlling for baseline serum creatinine and other variables, the presence or absence of baseline hyperuricemia (defined as >7 mg/dl in men and >6 mg/dl in women) markedly increased the risk for developing end stage kidney disease requiring dialysis. (b) A figure based on the study of 5707 participants aged 20 years and older from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. There is an exponential relationship of serum uric acid levels with CKD. (a) Adapted from Iseki et al.7 and (b) Adapted from Zhu et al.8 CKD, chronic kidney disease; HyperUric, hyperuricemia.