Figure 5.
Discovery of cell-type-specific molecular networks and significant ligand-receptor interactions in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) using autoCell
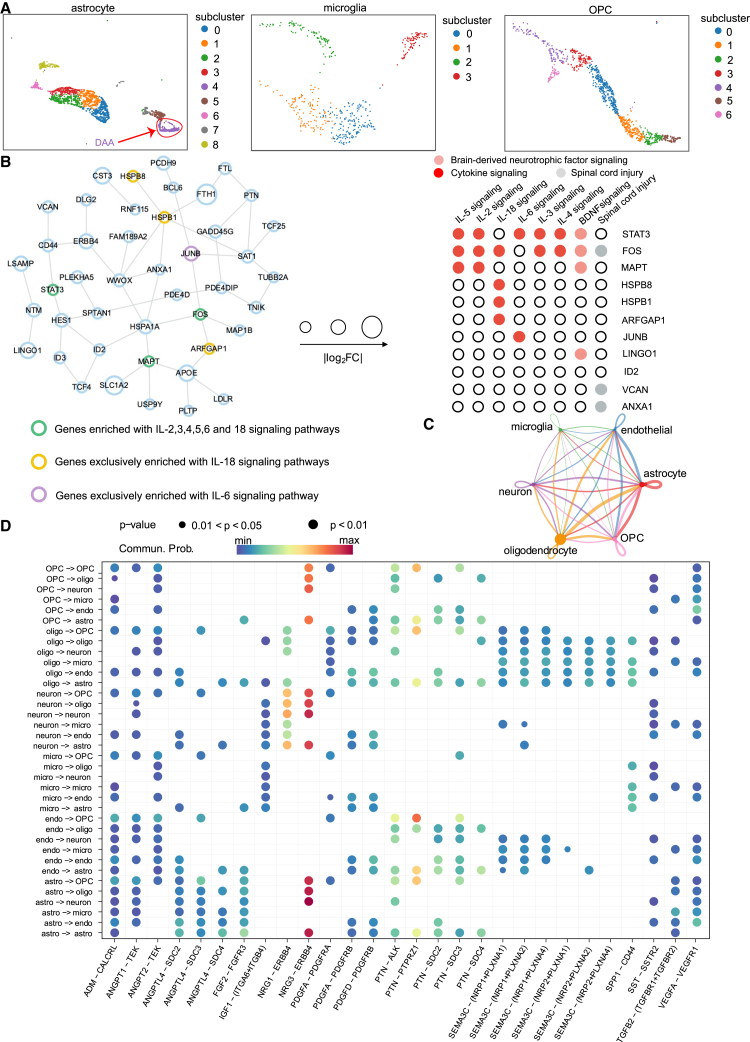
(A) UMAP visualization of subclusters of astrocytes (including disease-associated astrocyte [DAA]), microglia, and OPCs, labeled with autoCell clusters.
(B) Reconstruction of the DAA-specific molecular subnetwork from the human protein-protein interactome. The DAA-specific module network included 50 protein-protein interactions (PPIs) connected by 44 proteins (e.g., APOE, MAPT, CD44, FOS, and STAT3). The proteins from the DAA-specific molecular network are enriched with multiple AD-related pathways, including cytokine signaling pathways. The proteins from the DAA-specific molecular network are enriched with multiple cytokine signaling pathways.
(C) Inferred cell-cell interactions using CellChat.
(D) Top selected significant ligand-receptor pairs among autoCell-identified cell types. Ligand-receptor interactions were predicted by CellChat (see STAR Methods).