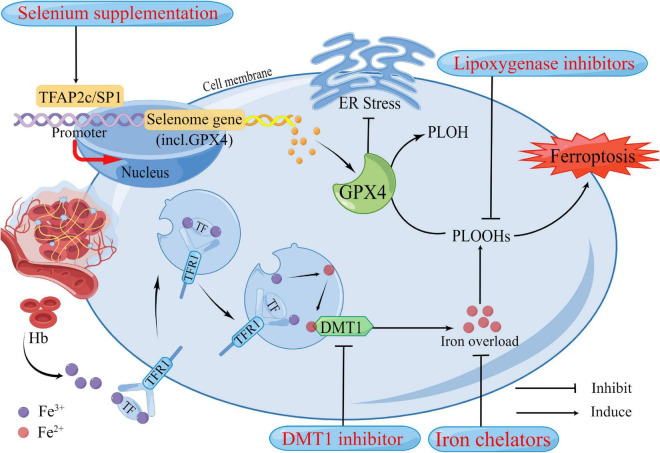
FIGURE 2.
Potential therapeutic strategies based on neuronal ferroptosis after Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Several regulators in the ferroptosis pathway are highlighted in the treatment of ICH. These regulators have been confirmed to play roles in ferroptosis. After ICH, in addition to the primary brain injury caused by the hematoma compressing the surrounding brain tissue, Hb, iron, and other neurotoxic substances released by the hematoma also contribute to the increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in ferroptosis and cause secondary brain injury. DMT1 and Iron chelators could reduce iron overload from two aspects, respectively. GPX4 acts as an antioxidant that inhibits ER stress and reduces lipid peroxides in cells to harmless PLOH to inhibit ferroptosis. It has been well established that GPX4 deficiency causes neuronal ferroptosis after ICH. Selenium supplementation augments GPX4 and other genes in this transcriptional program, the selenome, via coordinated activation of the transcription factors TFAP2c and Sp1 to protect neurons. Hb, hemoglobin; Fe3+, ferric iron; Fe2+, ferrous iron; TF, transferrin; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; Gpx4, glutathione peroxidase 4; PLOH, phospholipid alcohol; PLOOHs, phospholipid hydroperoxides; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.