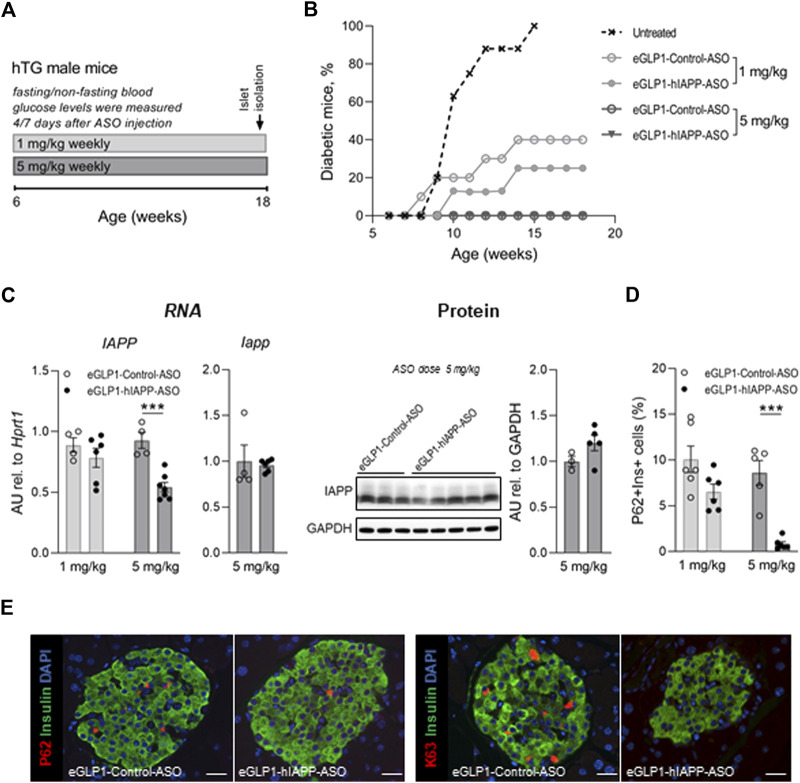
FIGURE 2.
Effect of treatment with eGLP1-hIAPP-ASO on diabetes development and autophagy/lysosome dependent pathway of protein degradation in beta cells. (A) Scheme of the experiment. Mice were treated weekly with eGLP1-hIAPP-ASO or with eGLP1-Control-ASO (eGLP1 peptide conjugated to an ASO with a scrambled nucleotide sequence). (B) Diabetes development (mouse was considered to be diabetic if blood glucose levels measured after overnight was >125 mg/dl or non-fasting morning glucose aver 250 mg/dl). (C) Islet hIAPP RNA levels were decreased in dose dependent manner without noticeable effect on levels of the monomeric hIAPP protein relative to e-GLP1-Control-ASO treated mice. (D) The frequency of beta cells containing P62 positive inclusions decreased in eGLP1-hIAPP-ASO treated mice in a dose dependent manner. (E) Representative images of islets stained for P62 and K63 polyubiquitinated proteins destined for the autophagosome/lysosome mediated degradation (scale bar 25 mm). (C–E) Data are from non-diabetic mice only. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 5–7 in (b), n = 4–6 in (c); n = 5–6 in (f); *** - p <0.001, two-tailed non-paired Student’s test; hTG—human IAPP transgenic.