Extended Data Fig. 1. ATX and PRG-1 expression in cortical neurons.
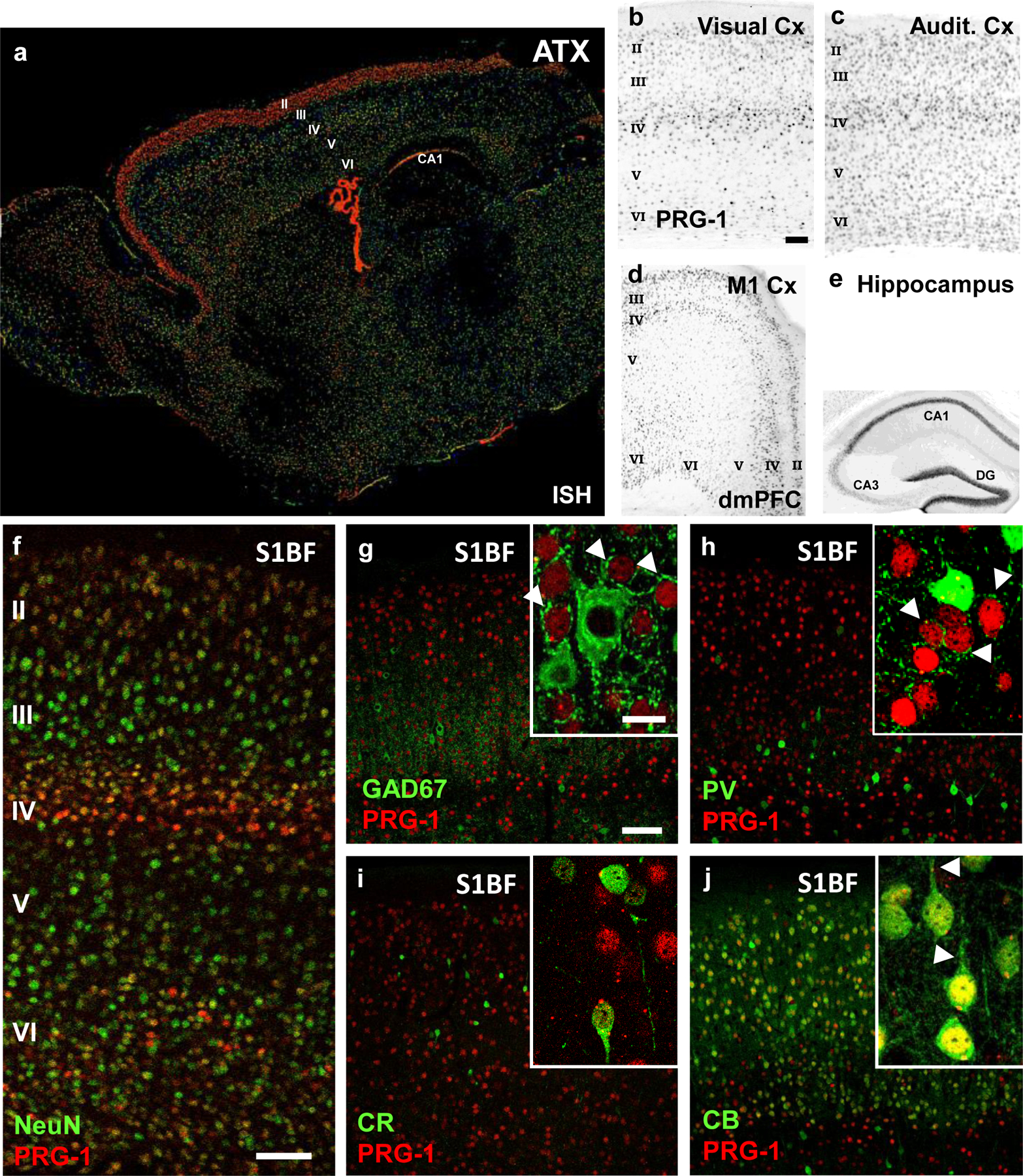
a. ATX expression as shown by in-situ hybridization is present in the cortex and in the choroid ventricular plexus. Interestingly, strong expression in the cortex can be observed in the upper cortical layers (most prominent in layer II), which are important for cortical information processing. Image from the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas (mouse.brain-map.org).
b-f. PRG-1 expression, as demonstrated by the ß-Gal reporter (for genetic details see Trimbuch et al., 2009), is predominantly found in the layers 2/3, 4 and 6 of the neocortex (visual cortex [A], auditory cortex [B], primary motor cortex [M1, C], dorsomedial prefrontal cortex [dmPFC,C] and primary sensory cortex [S1BF, F]). Strong expression was also found in the hippocampal formation (shown in E), as previously demonstrated.
g-i. Staining for inhibitory neurons (GAD67, parvalbumin [PV] and calretinin [CR]) in the primary somatosensory cortex revealed no expression of PRG-1 in interneurons. Note the strong perisomatic inhibitory synapses of the excitatory, PRG-1-expressing neurons (arrowheads in the inserts in G and H).
j. PRG-1 expression was detected in pyramidal (excitatory) neurons of the layer II, which express calbindin. Note the clear apical dendrites of these pyramidal neurons (arrowheads).
Scale bars: b-e 250 µm, f-j 100µm, insets 15 µm.
