Extended Data Fig. 5. Altered synaptic lipid signaling is associated with increased body weight in mice and humans.
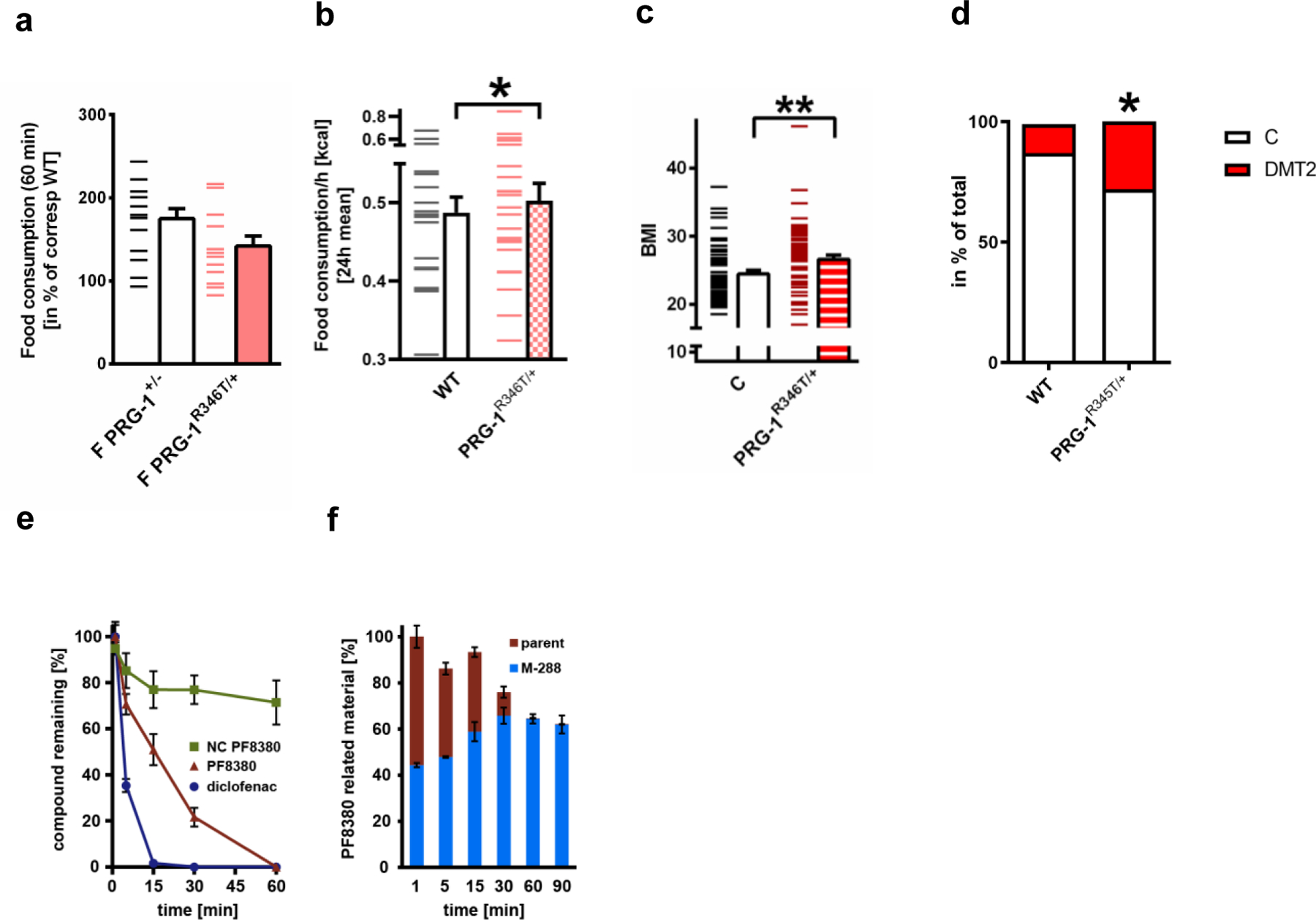
a. Fasting induced hyperphagia was not different in PRG-1+/- and PRG-1R346T/+ animals (n = 14 PRG-1+/- and n = 13 PRG-1R346T/+, two-sided t-test, dashes represent single values, bars represent mean and s.e.m)
b. Baseline food consumption per hour averaged for a 24h interval revealed significant higher food intake in PRG-1R346T/+ animals when compared to WT littermates (n = 20 WT and n = 23 PRG-1R346T/+ mice, group differences 86,7%, Bayesian analysis.
c. BMI was significantly increased in human PRG-1R345T SNP monoallelic mutation carriers (n = 58 PRG-1R346T/WT and n = 60 PRG-1WT sex, age, height and education matched controls, P = 0.0041, two-tailed t-test, **p<0.01). A-E: Bars represent mean and SE.
d. Diabetes type 2 (DMT2) prevalence was significantly increased in male PRG-1R346T/WT carriers, which displayed a significantly higher odds ratio (OR) for DMT2 of 2.45 (p = 0.037, logistic regression was adjusted for age, sex and cohort)(n = 3947 control cohort with 443 individuals with diabetes; n = 32 PRG-1R345T/WT mutation carriers with 7 individuals with diabetes; P = 0.0291, chi square test, p*<0.05). For better comparison, graph shows number of diabetic individuals as a percentage of the corresponding group.
e,f. PF8380 was quickly metabolized by human liver microsomes (n = 3; CLint >100 µl∙(min ∙ mg)-1, diclofenac was used as a positive control. PF8380 was mainly degraded to a putative metabolite with 288 g∙mol-1.
Dashes represent single values, bars represent mean and SEM.*p<0.05, **p<0.01, or group differences of * >80% for Bayesian analysis..
