Figure 2.
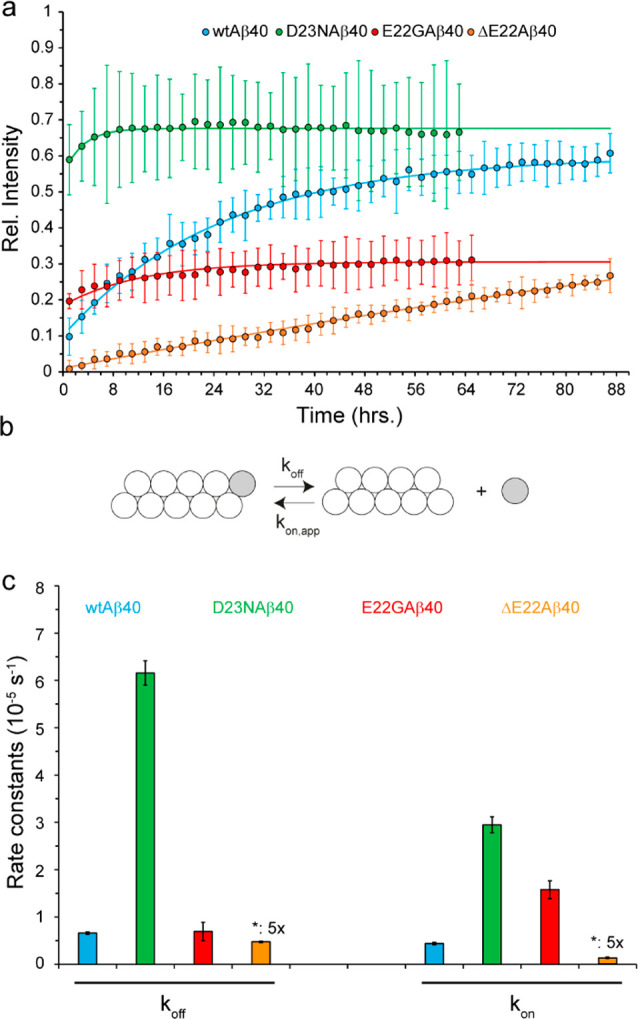
Stability of Aβ40 aggregates against high pressure. (a) Pressure-induced monomer release from Aβ40 aggregates, as followed by real-time NMR experiments at 2000 bar, 278 K, through average (±SD) peak intensities. (b) A simple kinetic model of Aβ40 disaggregation, involving only two states (aggregate state, monomer state) and two rates (dissociation, koff, and back-association, kon). (c) Rate constants obtained from the analysis of monomer release kinetic data shown in (a), according to the simple model shown in (b). The D23N-Aβ40 variant showed much larger koff and kon rates than the wild-type variant, while the ΔE22-Aβ40 variants showed smaller koff and kon rates. See the text for further details and interpretations. For the sake of visibility, the rate constants of ΔE22-Aβ40 are multiplied by a scaling factor of 5. The error bars represent fitting errors.
