Figure 3.
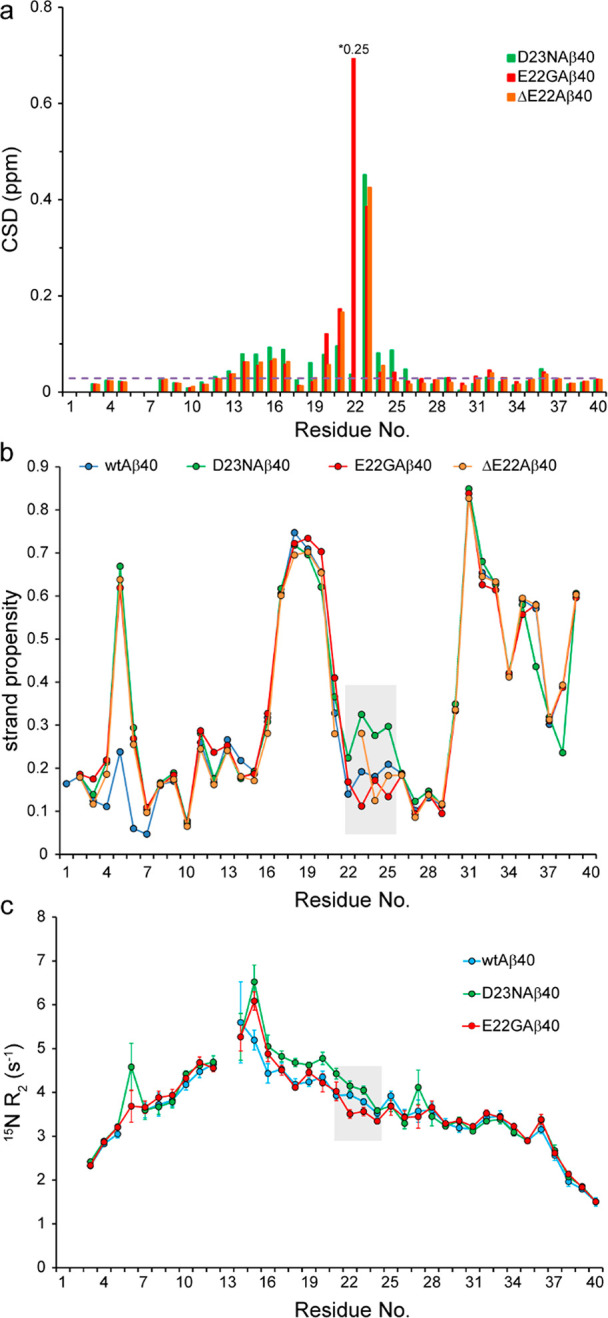
Effect of FAD mutations on the structure and dynamics of Aβ40 variants. (a) Combined 15N and 1H chemical shift deviation (CSD) of D23N-, E22G-, and ΔE22-Aβ40 peptides with respect to the wild-type-Aβ40, showing significant chemical shift differences around the respective mutation sites and to a lower extent around residues H14-L17. The dashed line represents the noise level in chemical shift values. For the sake of visibility, the CSD value of residue 22 in the E22G-Aβ40 peptide has been scaled down by a factor of 4. (b) The strand propensity of wild-type-, D23N-, E22G-, and ΔE22-Aβ40, calculated on the basis of their backbone (CO, Cα, N, HN, Hα) plus Cβ chemical shifts. The shaded area shows how the respective mutations alter the strand propensity around the site of mutation (see also Supplementary Figure S3). (c) Residue-specific 15N transverse relaxation (R2) rates of Aβ40 variants measured at 278 K. Note the larger R2 of D23N-Aβ40 and smaller R2 of E22G-Aβ40 around the mutation site (shaded area), indicating respectively their relative rigidity and flexibility when compared with the wild-type-Aβ40. The relative rigidity of the D23N-Aβ40 variant extends further proximally to Q15-K16.
