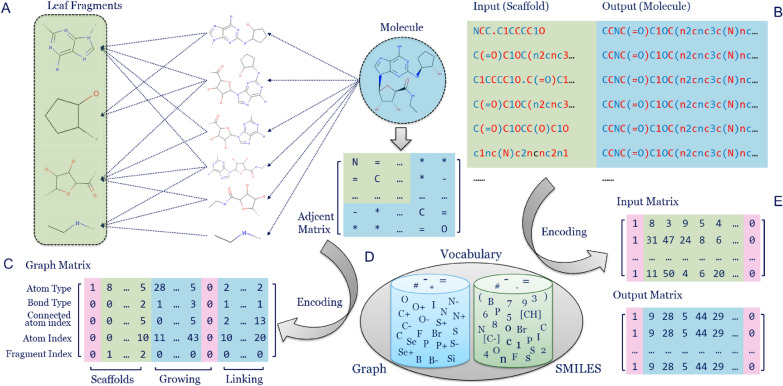
Fig. 1.
scaffold-molecule pair dataset construction. (A) Each molecule in the dataset is decomposed hierarchically into a series of fragments with the BRICS algorithm. (B) Subsequently data pairs between input and output are created. Combinations of leaf fragments form the scaffold as input, while the whole molecule becomes the output. For clarity token colors alternate. (C) After conversion to an adjacency matrix, each molecule was represented as a graph matrix. The graph matrix contains five rows, standing for the atom type, bond type, connected atom index, atom index, and fragment index. Columns are divided in three parts to store the information of the fragment, the growing section and the linking section. (D) All tokens are collected to construct the vocabularies for SMILES-based and graph-based generators, respectively. (E) An example of the input and output matrices for the SMILES representation of scaffolds and molecules.