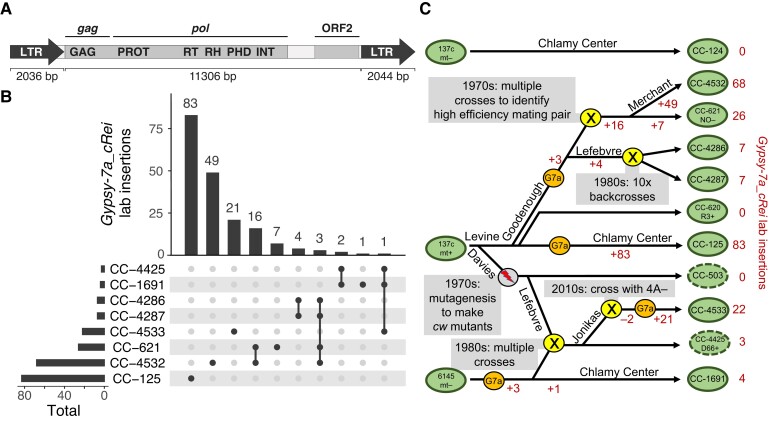
Figure 6.
Gypsy-7a_cRei insertions and the strain history of 137c+. A, Structure of the 15.4-kb Gypsy LTR retrotransposon. LTR subparts are shown as block arrows; note that the left LTR is missing the final 8-bp of the right LTR. The two ORFs are highlighted within the 11.3-kb internal section, and the gag and pol sections of the polyprotein are indicated. Protein domains: GAG, group-specific antigen; PROT, pepsin-like aspartate protease; RT, reverse transcriptase; RH, RNAse H; PHD, plant homeodomain finger; INT, integrase. B, Upset plot (Lex et al. 2014) showing the number of shared and strain-specific laboratory insertions of Gypsy-7a_cRei in select laboratory strains. Ancestral copies of Gypsy-7a_cRei are excluded. C, Schematic diagram representing a putative strain history of several interrelated laboratory strains. Presented is the most parsimonious interpretation of the shared and independent insertions (B) coupled with known strain histories. Green ovals represent strains as indicated, with a dashed line indicating cell wall defective strains. A gray circle indicates the MNNG mutagenesis that produced cw mutants. Yellow circles indicate crosses as labeled. Orange circles indicate likely activation of Gypsy-7a_cRei (“G7a”). Changes in the net number of Gypsy-7a_cRei loci due to addition by retrotransposition (+) or loss during crossings (−) are indicated in red. The names of several key Chlamydomonas researchers (R.P. Levine, D.R. Davies, U.W. Goodenough, P.A. Lefebvre, S.S. Merchant) are indicated where relevant.