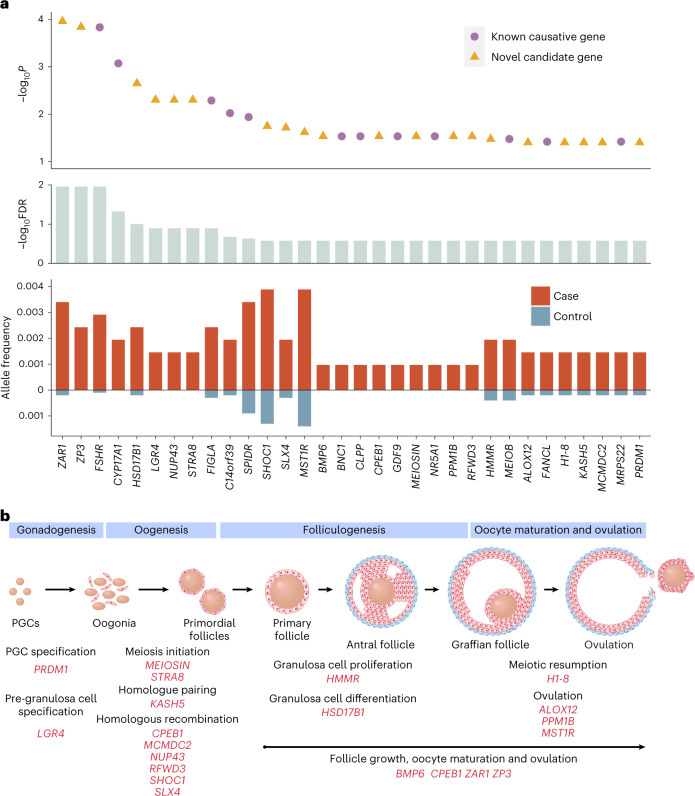
Fig. 3. Discovery of novel causative genes through large case–control association analysis of POI.
a, LoF variants in 32 genes were enriched in cases with POI when compared with controls (cases n = 1,030; controls n = 5,000). Genes with FDR < 0.3 are shown. The upper graph shows P values for difference in the prevalence of LoF variants between cases and control individuals generated by one-sided Fisher’s exact tests; middle graph shows FDR; lower graph displays the allele frequency of LoF variants in each gene. b, Overview of 20 novel genes with LoF variants significantly enriched in POI. The upper graph is a schematic representation of the ovary development process, categorized into four stages: gonadogenesis, oogenesis, folliculogenesis and oocyte maturation and ovulation. The lower graph depicts the physiological roles and molecular mechanisms throughout ovary development of 20 significantly enriched genes. LGR4 and PRDM1 are involved in gonadogenesis; KASH5, CPEB1, MCMDC2, MEIOSIN, NUP43, RFWD3, SHOC1, SLX4 and STRA8 are involved in various meiotic processes; and ALOX12, BMP6, CPEB1, H1-8, HMMR, HSD17B1, MST1R, PPM1B, ZAR1 and ZP3 are involved in follicle development, oocyte maturation and ovulation. Genes may be engaged in multiple processes.