Figure 2.
Analysis of protein synthesis in the cytosol and cytomatrix
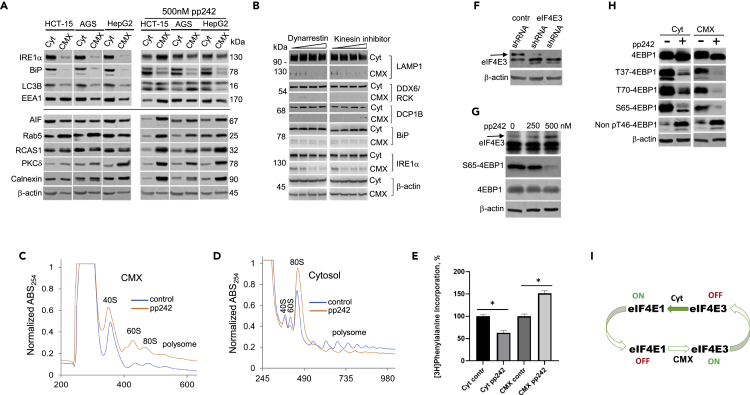
(A) Protein distribution in the cytosol and cytomatrix of three cell lines under the normal growth conditions (left panel) and 500 nM of pp242 treatment for 24 h (right panel).
(B) The effect of increasing concentration of motor protein inhibitors on protein distribution in the cytomatrix and cytosol of HCT-15 cells. Inhibitors of the dynein and kinesin proteins showed no effect on protein distribution. To minimize mixing during loading, the equal amounts of samples were run separately. Side by side running gel data for the same samples are presented in Figures S3A and S3B.
(C and D) Polysome profile of the cytomatrix and cytosol of HCT-15 cells.
(E) The incorporation of radiolabeled L-[3H]-phenylalanine into proteins of the cytosol, and the CMX in untreated and pp242-treated HCT-15 cells. L-[3H]-phenylalanine was added, and cells were incubated for 1 h. ∗p-value of one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001. Data are given as means ± SE, n = 5.
(F) eIF4E3 is localized in the cytomatrix of HCT-15 cells.
(G) The pp242 increased eIF4E3 protein expression in the CMX of HCT-15 cells.
(H) eIF4E-BP1 phosphorylation in the cytosol and cytomatrix with and without pp242 treatment of HCT-15 cells.
(I) Hypothetical diagram of inverse relationship of the eIF4E1 and eIF4E3. eIF4E – eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. BP1 – eIF4E binding protein 1.