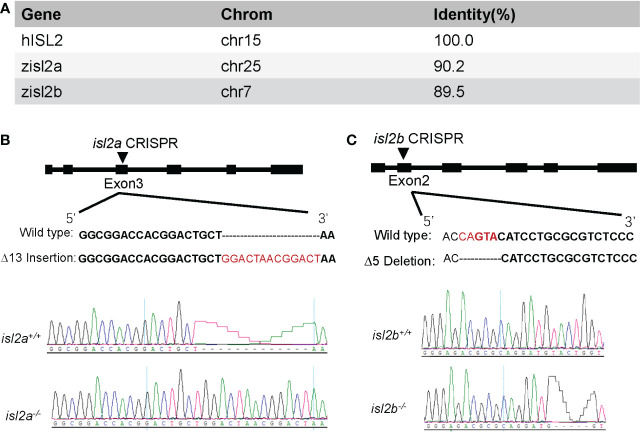
Figure 1.
Generation of isl2a and isl2b knockout zebrafish utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 technology. (A) Amino acid identity between zebrafish and human ISL2 proteins was performed using UCSC Blat software. (B) The isl2a-CRISPR-target site (black bold words) was designed in exon3 of isl2a and the CRISPR/Cas9-induced insertion of 13 nucleotides (red words) was selected for further investigation. (C) In the case of isl2b, the CRISPR-target site (bold words) was designed in exon2, and the induced deletion of five nucleotides (red words) was selected for further investigation. Genotypes, including wild-type and homozygotes, were analyzed and shown in the bottom panel. Both genotypes were predicted to produce truncated proteins.