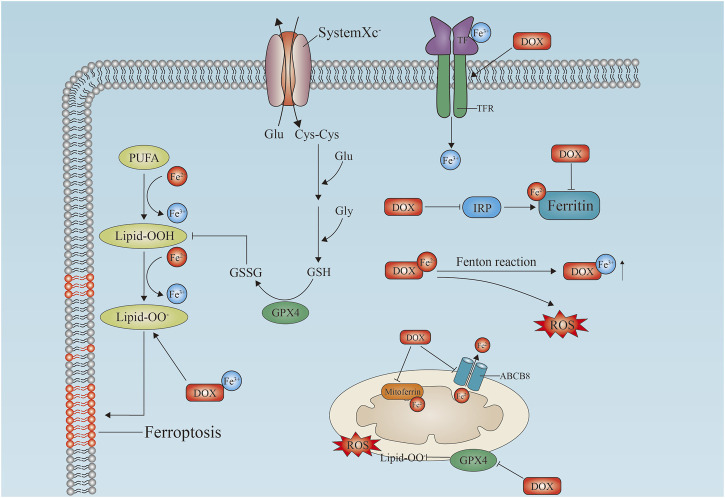
FIGURE 2.
Doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Schematic diagram of the doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis pathway in cardiomyocytes. Doxorubicin upregulates TfR and inactivates ferritin, which induces lipid peroxidation by inhibiting GPX4 in cell membranes and mitochondria, leading to ferroptosis. Free iron binds to doxorubicin to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). In mitochondria, doxorubicin causes iron overload by blocking MitoFer and ABCB8. IRP, iron response regulatory protein; Tf, transferrin; TfR, transferrin receptor; Lipid-OO, lipid peroxidation; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GPX4, glutathione Peroxidase; MitoFerrin, mitochondria ferritin; ABCB8, ATP-binding cassette transporter eight; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DOX, doxorubicin.