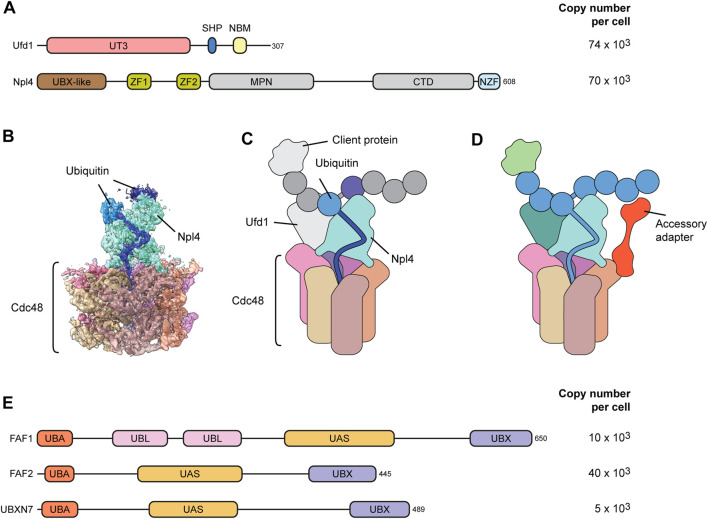
FIGURE 3.
Adapter and accessory adapters for ubiqutin-mediated targeting. (A) Domain structure of the major Ufd1-Npl4 client adapter. Ufd1-Npl4 is a heterodimer that binds p97 cooperatively via interactions of a UBX-like (UBXL) domain in Npl4 and a SHP box in Ufd1 with p97 N-domains. The zinc fingers (ZF1 and ZF2) in Npl4 make contact with the top of the D1 ring. The UT3 domain in Ufd1 and the C-terminal domain (CTD) in Npl4 bind and position the ubiquitin chain. The ubiquitin-binding NZF is specific for metazoan Npl4. NBM, Npl4 binding motif. MPN, Mpr1, and Pad1 N-terminal domain. Copy numbers of indicated proteins compared to roughly 230 × 103 p97 hexamers in human U2OS osteosarcoma cells according to (Beck et al., 2011). (B) Cryo-EM structure (pdb 6OA9 and EMD-0665) of yeast Cdc48-Ufd1-Npl4 with a ubiquitinated model substrate in the central pore. Dark blue depicts one unfolded ubiquitin moiety bound to a groove in Npl4 (cyan). Additional ubiquitin moieties are bound on top. (C) Cartoon model of the structure in (B). Ufd1, the client and additional ubiquitin moieties are not resolved in the structure. (D) Speculative model for the function of accessory adapters such as FAF1, FAF2 or UBXN7. Accessory adapters enhance p97 affinity for the client by bridging p97 with the ubiquitin chain attached to the client, thereby assisting Ufd1-Npl4-mediated client targeting and unfolding. (E) Domain structure of p97 cofactor proteins that have been proven to act as accessory adapters cooperating with Ufd1-Npl4. They are characterized by UBX and UBA domains that bind p97 and ubiquitin, respectively, and possess a thioredoxin-like (UAS) domain of yet unknown function. UBL, ubiquitin-like domain.