Fig. 2. Arsenic causes different pro-atherogenic changes depending on the type of macrophages.
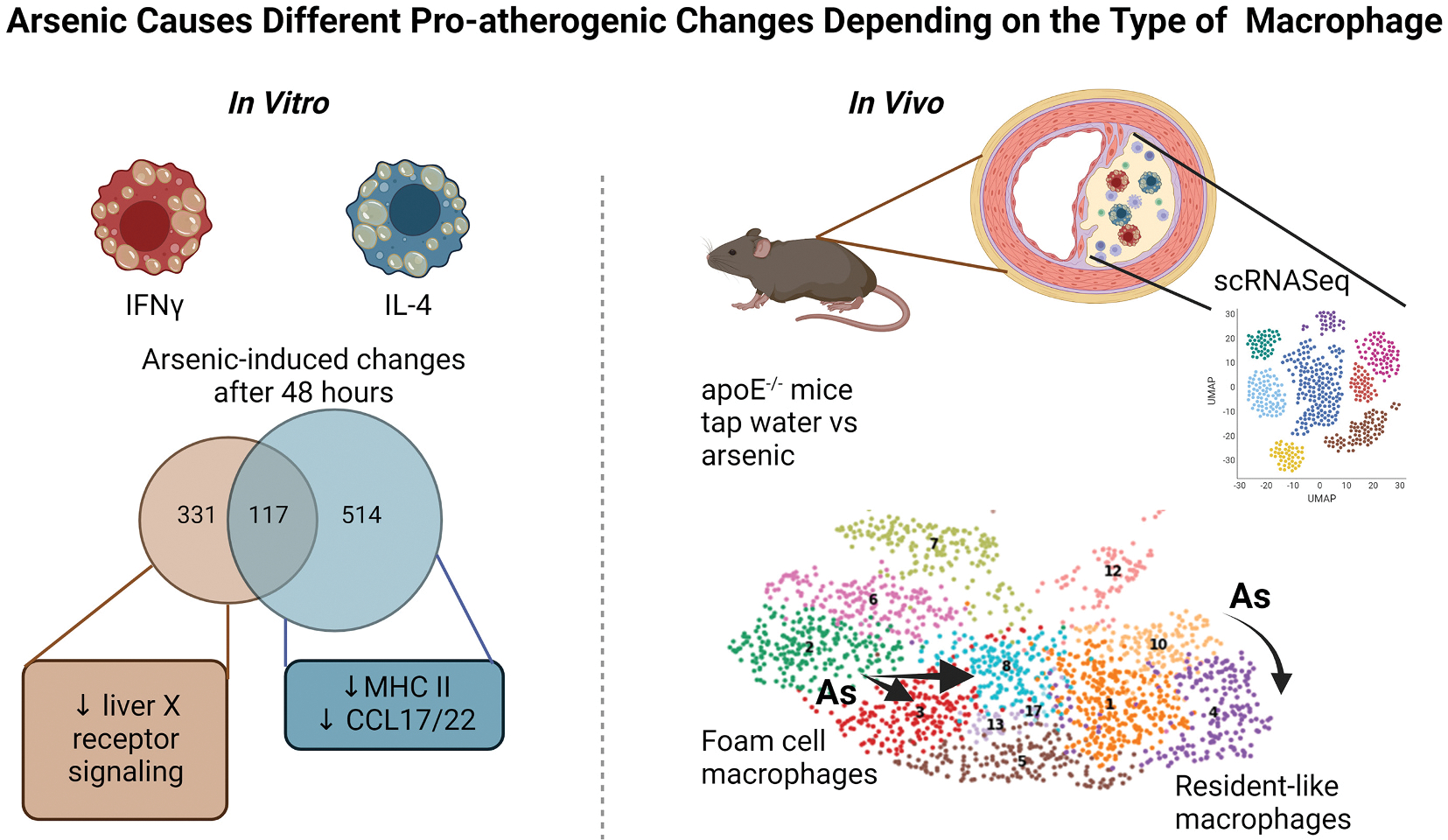
In vitro, macrophages polarized with either IFNγ or IL-4 for 48 h in the presence or absence of arsenic were analyzed by bulk RNA sequencing. Arsenic induced different gene expression changes depending on the polarization. For example, arsenic decreased liver X receptor signaling in IFNγ-stimulated macrophages, but not in IL-4-stimulated macrophages. Arsenic decreased MHC II and CCL17/22 in IL-4-stimulated macrophages, but not IFNγ. In vivo, cells from the atherosclerotic plaques of ApoE−/− mice (tap water versus 200 ppb arsenic for 13 weeks) were isolated and analyzed by single cell RNA sequencing (scRNASeq). Foam cell macrophages in control animals (green cluster 2) increased heterogeneity (to red cluster 3 and light blue cluster 8). Resident-like macrophages changed from yellow cluster 10 (control) to purple cluster 4 (arsenic). However, these changes were distinct and dependent upon the original cluster from which they were derived. (Figure created with Biorender).
