Fig. 3. Cardiac effects of low-dose Cd exposure with and without the second stress, HFD or Western diet.
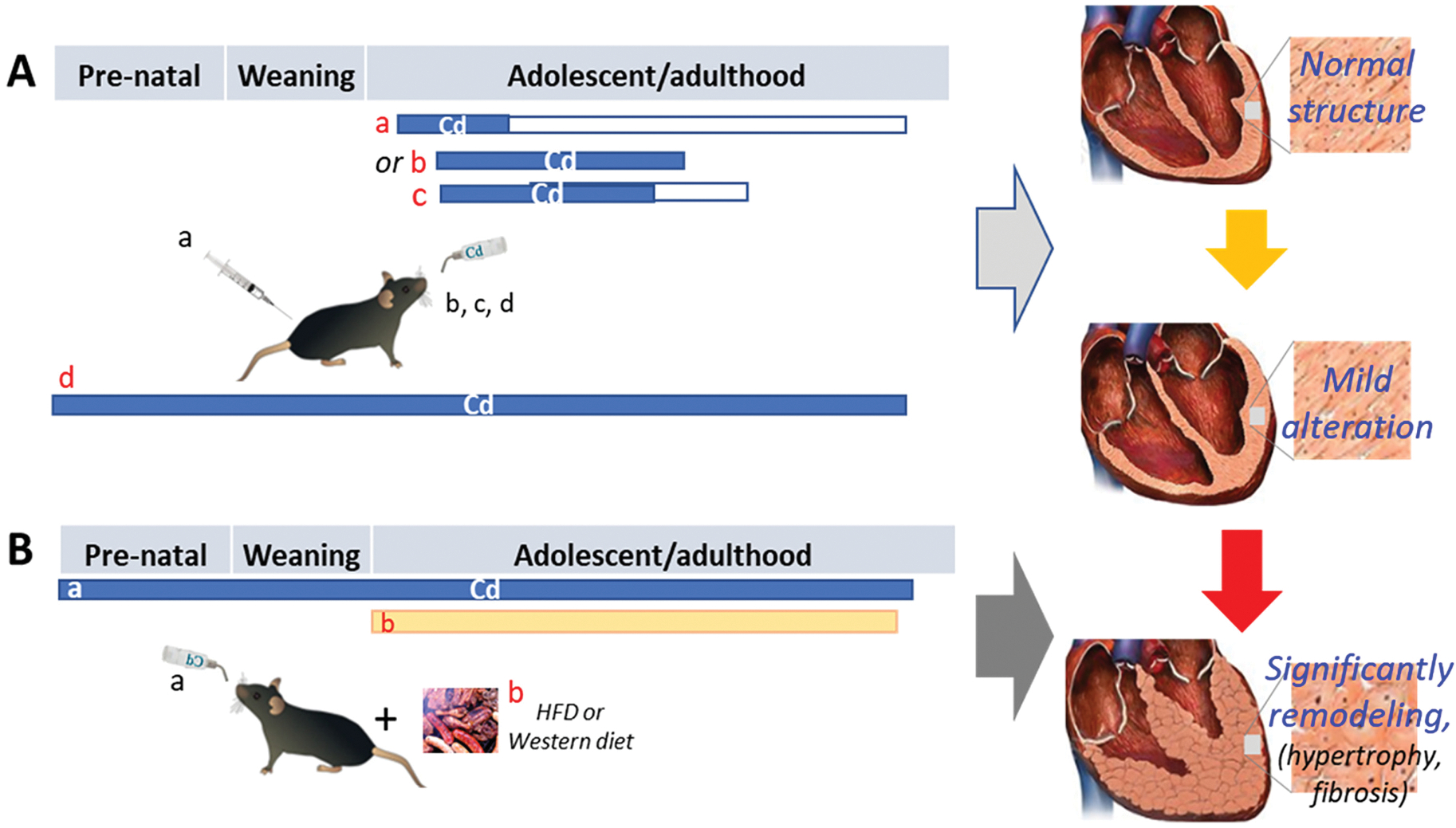
The experimental designs were briefly described for a few studies, for which mice and rats were chronically exposed to low-dose Cd (blue bar) either intraperitoneally or in the drinking water at different stages of life for various durations. In panel A: a, starting at 6 week (wks) old and continuing for 4 wks only, followed by abstaining Cd for 56 wks (white box); b, starting at 8 wks old and continuing for 12 wks; c, starting at 8 wks old and continuing for 10 wks, followed by abstaining Cd for 4 wks; d, whole-life Cd exposure until sacrifice. All four strategies caused only mild cardiac pathogenesis without significant cardiac dysfunction. In Panel B: the exacerbated effects of whole-life exposure to low-dose Cd in the drinking water (blue bar) on post-weaning HFD- or Western diet (yellow bar)-induced cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. This illustration was made based on the experimental models and outcomes by Turdi et al. (Panel A-a), Turkcan et al. (Panel A-b), Das et al. (Panel A-c), Liang et al. (Panel A-d, Panel B, Western diet), and Zhou et al. (Panel A-d, Panel B, HFD).
